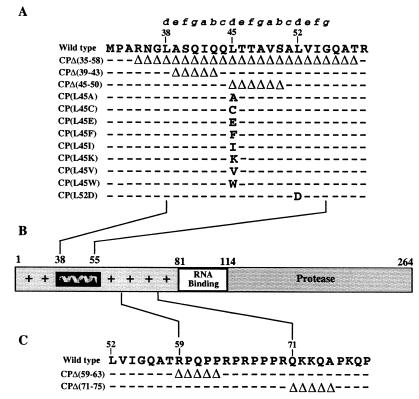
FIG. 3.
(A) Amino acid deletions and substitutions in helix I. The wild-type sequence corresponds to residues 32 to 59 of the SINV CP. Deletions (▵) and substitutions are indicated. Dashes indicate the wild-type sequence. Mutations were generated using the new restriction sites in the pToto71 cDNA clone of SINV as described in Materials and Methods. (B) Schematic diagram of the SINV CP. Residues 1 to 80 have a high degree of positive charge and are implicated in nonspecific recognition of the RNA, with the exception of residues 38 to 55, which are uncharged and form helix I. Residues 81 to 113 contain important determinants that are involved in specific recognition of the genomic RNA. Residues 114 to 264 form the protease domain and are also involved in capsomeric contacts as well as contacts with the cytoplasmic domain of E2. (C) Amino acid deletions outside helix I. Mutations were constructed by oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis in the pToto63 cDNA clone of SINV as previously described (30).