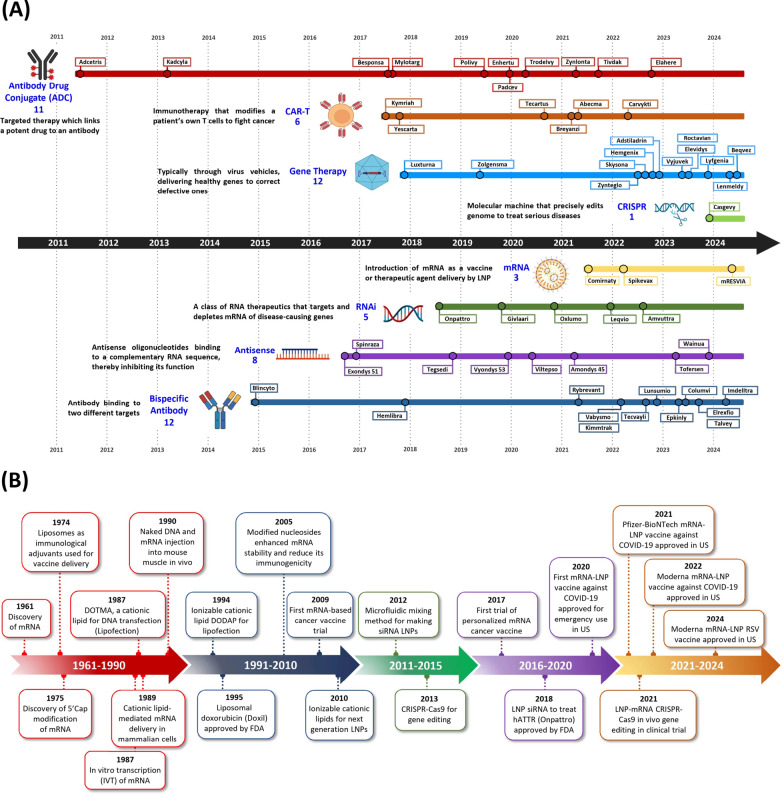
Fig. 1.
A Overview of new US FDA-approved therapeutic modalities. Recent technological breakthroughs have led to the introduction of several new therapeutic modalities and are expected to drive further innovation in the biopharmaceutical industry over the coming decades. The schematic illustrates a spectrum of new pharmaceutical modalities encompassing eight distinct categories: Antibody–Drug Conjugates (ADCs), gene therapy, chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR T) therapy, CRISPR-based therapeutics, messenger RNA (mRNA) therapeutics, small interfering RNA (RNAi), antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), and bispecific antibodies. Prominent examples of pioneering US FDA-approved drugs within each modality are listed as follows. ADCs: Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin, approved 2011), bispecific antibodies: Blincyto (blinatumomab, approved 2014), RNAi: ONPATTRO (patisiran), ASOs: Exondys 51 (eteplirsen, approved 2016), CAR T therapy: Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel, approved 2017), Gene therapy: Luxturna (voretigene neparvovec-rzyl, approved 2017), mRNA therapeutics: Pfizer-BioNTech's Comirnaty (COVID-19 Vaccine, BNT162b2, approved 2021). Furthermore, the recent approval of a CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing therapy, Casgevy (exagamglogene autotemcel, approved December 8, 2023), underscores the continual expansion of therapeutic modalities. Numerous new cutting-edge technologies including mRNA technologies are currently under evaluation at various stages of drug development. B The graphic outline of milestones and development timeline in mRNA technologies and LNP delivery systems