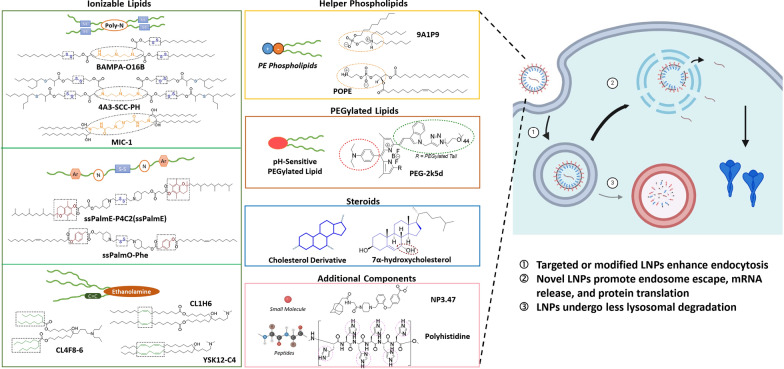
Fig. 4.
Strategies to facilitate endosomal escape of LNPs for enhanced mRNA release and protein translation. LNPs are taken up into cells via endocytosis. Targeted or modified LNPs can enhance endocytosis. Innovative ionizable lipid structures used in the formulation of LNPs can facilitate endosomal escape and release of the payload into the cytosol. The integration of cutting-edge ionizable lipid structures within LNPs can significantly enhance endosomal escape, facilitating the efficient release of the encapsulated payload into the cytosol. Novel ionizable lipids commonly feature distinctive characteristics, such as a polyamine head group with a pKa around 6.5, incorporation of aromatic ring moieties in linker chains, and diverse tail compositions (e.g., bioreducible disulfide, branched, or unsaturated tails). Different helper lipids, such as PE-containing phospholipids, pH-sensitive PEGylated lipids, and hydroxylated cholesterol derivatives can contribute to endosomal escape as well. Integration of other materials, such as the small molecule inhibitor NP3.47 or polyhistidine peptides can also promote this process. Novel LNPs with these features have been shown to enhance endosomal escape and reduce lysosomal degradation of mRNA cargoes, which eventually promotes mRNA escape from endosomes and facilitates mRNA release, ultimately increasing translation of the encoded protein. Created with BioRender.com