FIGURE 3.
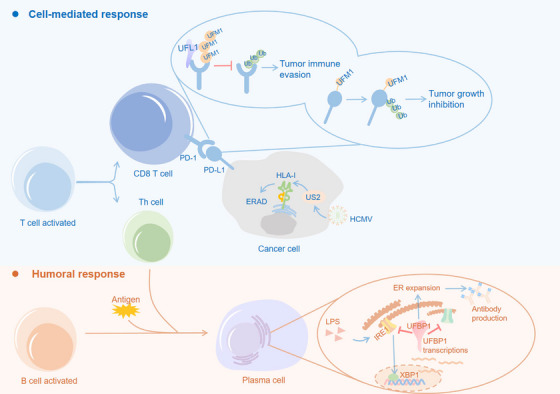
Functional regulation of UFMylation in adaptive immunity. UFMylation has emerged as a key regulator in tumour progression through modulating PD‐1/PD‐L1 signalling pathway. UFMylation tags PD‐L1 for proteasome‐mediated degradation to inhibit tumour growth. 10 UFL1 interacts with PD‐1 to promote its UFMylation, stabilising PD‐1 and impairing CD8+ T‐cell activation. 11 B‐cells stand as pivotal players in the generation of specific antibodies. The differentiation of plasma B cells stimulates a transcriptional increase of UFBP1 through XBP1s pathway. Serving as a feedback inhibitor, UFBP1 constrains the activity of sensors IRE1 and PERK, fostering ER expansion and immunoglobulin production. 12 Classical HLA‐I molecules bind with antigens and present them to T cells. The UFM1 system accelerates ERAD of HLA‐I with unraveling mechanisms, facilitating HCMV evasion from immune surveillance. 88
