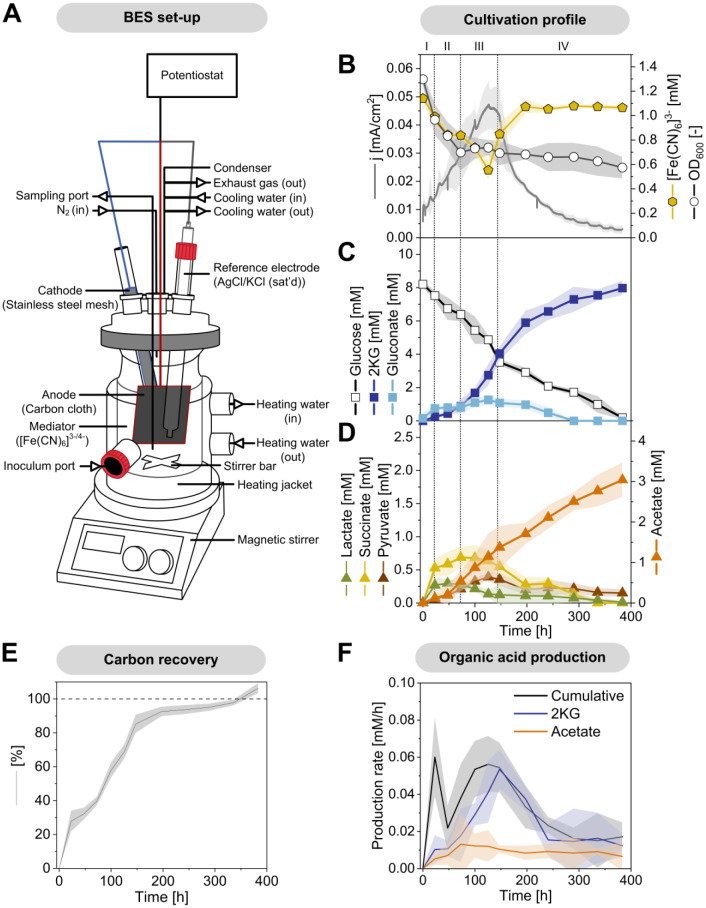
Fig. 1.
Bio-electrochemical fermentation of P. putida KT2440 on glucose. The bio-electrochemical reactor system (BES) comprised to compartments: The liquid volume of the anodic compartment containing the cultured cells was 320 mL. Ferricyanide, [Fe(CN)6]3−, was added to the medium as redox mediator. The reactor was operated at 500 rpm and 30 °C and sparged with N2 at a flow rate of 2 L h− 1. The potential of the working electrode was set to 0.5 V against the reference electrode (Ag/AgCl, in saturated KCl) (A). The data comprise the time profiles of current density (mA/cm2), cell concentration (OD600), and [Fe(CN)6]3− (mM) (B), glucose (mM), gluconate (mM), 2-ketogluconate (mM) (C), and other organic acids (mM) (D). The data were corrected for evaporation effects (Additional file 1) and used to estimate the carbon balance (E), as well as the yields and specific production rates of 2-ketogluconate, acetate, and cumulative acid production over time, respectively (F), n = 4