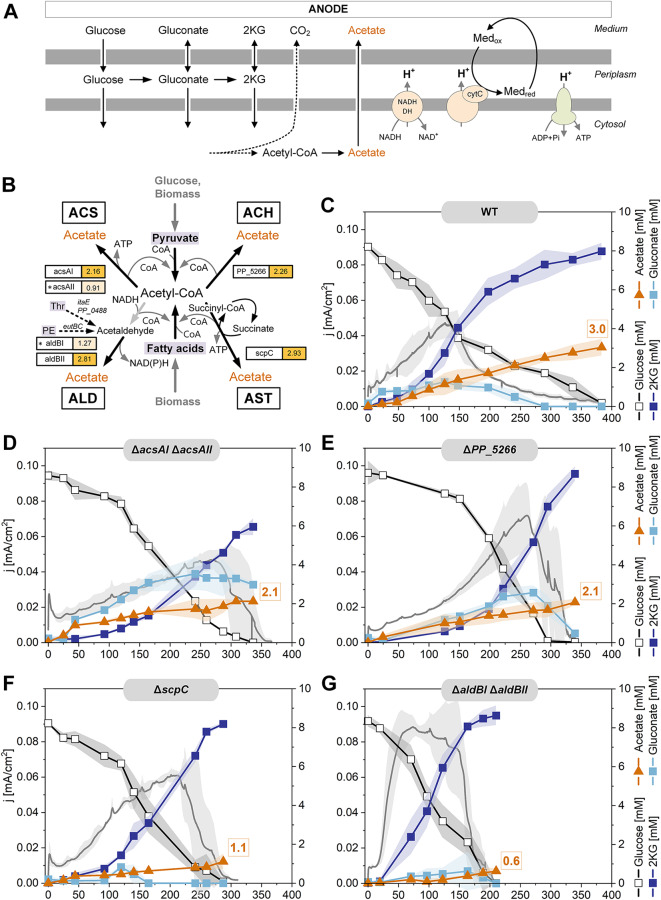
Fig. 8.
Impact of acetate production during bio-electrochemical fermentation of P. putida KT2440 on glucose. Schematic representation of the major energy-yielding pathways and processes under these conditions, including periplasmic glucose oxidation, cytosolic acetate formation, proton translocation by cytochrome c reductase and NADH dehydrogenase, respectively, and ATP generation by ATPase (A). Potential routes for acetate biosynthesis in P. putida KT2440, all originating from acetyl-CoA and connected to catabolic breakdown of glucose and biomass constituents (B). Fermentation profiles of KT2440 and deletion mutants, each lacking one of the four acetate biosynthetic routes (C-G). The data represent the current density (mA/cm2) and the concentrations of glucose, gluconate, 2-ketogluconate, and acetate, n = 4. Additional data on glucose and by-products are given in the Additional file 2