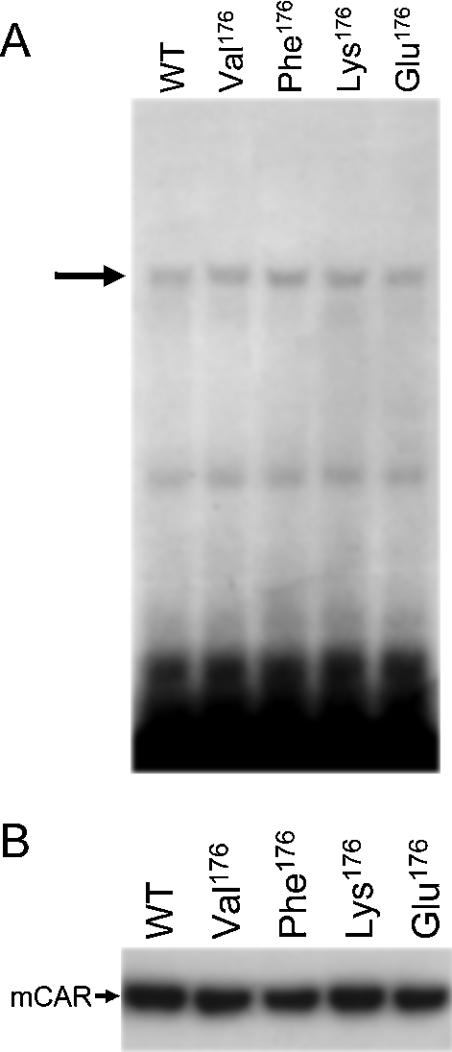
Figure 4. Intracellular localization and DNA-binding activity of mCAR and its mutants.
(A) Gel-shift analysis of mCAR and mutants. In vitro translated wild-type mCAR (WT) and various mutants (Val176, Phe176, Lys176 and Glu176) were incubated with 32P-labelled NR1. Mobility-shifted bands of NR1 caused by the formation of a complex between mCAR–hRXR are indicated by an arrow. (B) Western blotting detection of mCAR and its mutants (Val176, Phe176, Lys176 and Glu176) in nuclear extracts from HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells were transfected as described in the Experimental section, from which nuclear proteins were extracted and separated on an SDS/PAGE gel. Wild-type mCAR (WT) and the mutants were detected with anti-CAR polyclonal antibody.