Figure . aPLs bind to EPCR/LBPA and promote thrombosis and tissue damage.
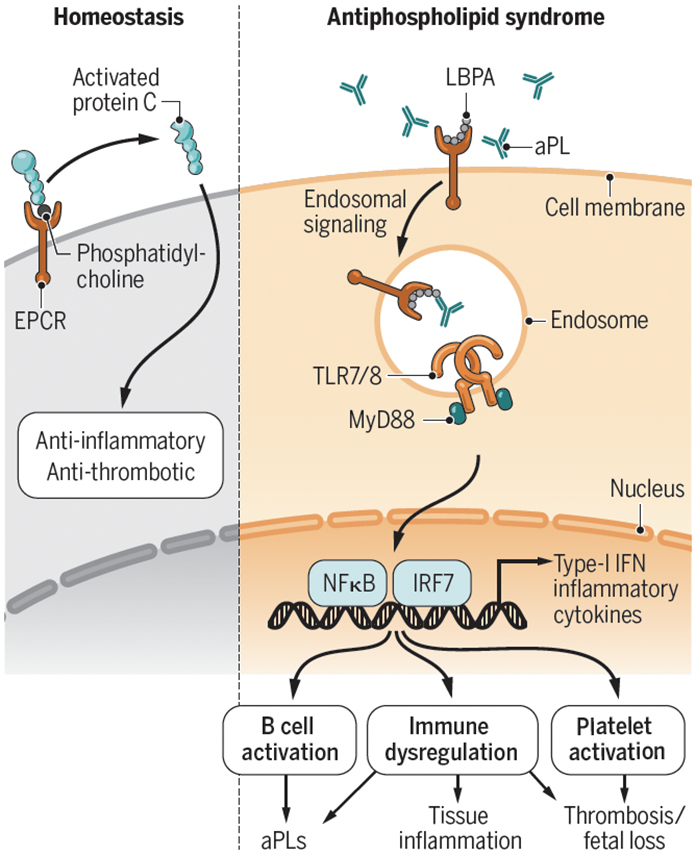
Under conditions of homeostasis, EPCR bound to phospholipids like phosphatidylcholine, activates protein C (PC) with downstream anti-thrombotic and anti-inflammatory effects. In contrast, lipid-reactive aPLs interact with EPCR bound to LBPA. This interaction promotes prothrombotic and proinflammatory responses, potentiation and activation of the endosomal TLR/type-I IFN pathway, further synthesis of autoantibodies and tissue inflammation, with effects on thrombosis and fetal loss.
aPL, phospholipid antibody; EPCR, endothelial protein C receptor; IFN, interferon; IRF7, interferon regulatory factor 7; LBPA, lysobiphosphatidic acid; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response protein; NFkB, nuclear factor-kb; TLR, Toll-like receptor.
