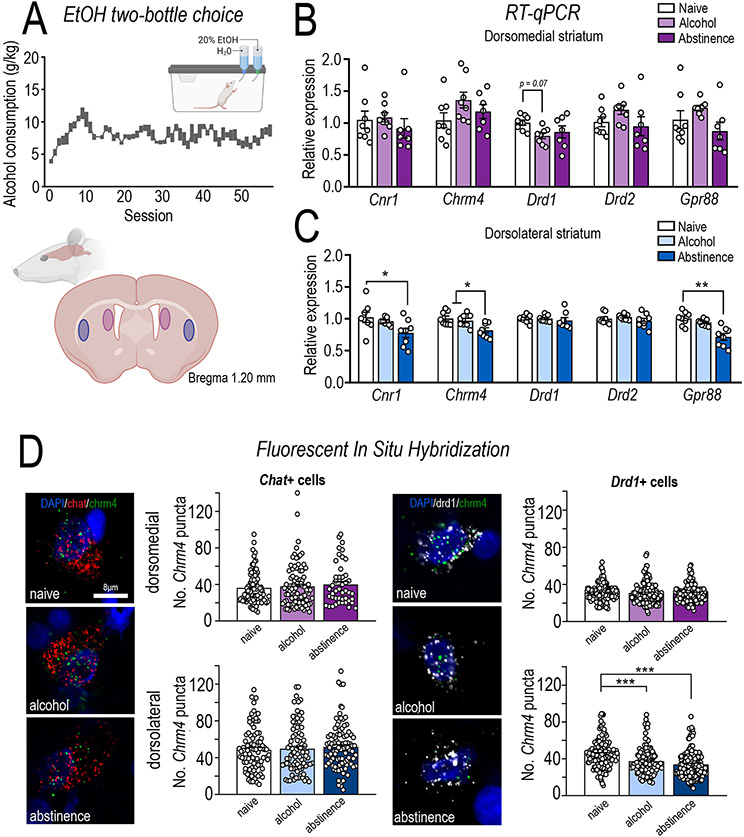
Figure 3. Molecular characterisation of the rodent dorsomedial and dorsolateral striatum following long-term alcohol consumption.
Alcohol preferring iP rats underwent long-term intermittent alcohol consumption in a two-bottle choice where they consumed (A) high levels of 20% alcohol (g/kg) across >57 sessions. Rats were randomly divided into two groups, one of which were culled 24 h after their final session (alcohol, n=8) and another which were culled 14 days after their last session (abstinence, n=8). A third group of age matched alcohol naïve rats were also included (n=8). The dorsomedial (DMS; caudate equivalent) and dorsolateral (DLS; putamen equivalent) striatum were assessed for molecular adaptations following long-term alcohol consumption and abstinence. RT-qPCR analysis was conducted in the (B) DMS and (C) DLS. In line with human post-mortem tissue from individuals with AUD, long-term alcohol consumption/abstinence in rodents decreased Chrm4 mRNA (ANOVA, F(2,21) = 6.955, p = 0.0048; Bonferroni post-hoc, naïve vs abstinence, p = 0.0064; alcohol vs. abstinence, p = 0.0279), Cnr1 (ANOVA, F(2,21) = 3.936, p = 0.0353; Bonferroni post-hoc, naïve vs. abstinence group, p = 0.0398) and Gpr88 (ANOVA, F(2,21) = 15.33, p < 0.0001; Bonferroni post-hoc, naïve vs. abstinence group, p < 0.0001; alcohol vs. abstinence, p = 0.0014) specifically in the DLS, without altering DMS mRNA expression. A trend towards DRD1 downregulated in the DMS was also observed (F (2,20) = 3.04, p = 0.0704; Bonferroni post hoc naïve vs. alcohol p = 0.0780). (D) M4 mAChRs are expressed on both direct pathway MSNs and cholinergic interneurons, therefore, to determine if Chrm4 mRNA is downregulated on direct MSNs (Drd1+) or cholinergic interneurons (Chat+) fluorescent in situ hybridization of Chrm4 expression was assessed. In line with RT-qPCR analysis, Chrm4 expression was specifically downregulated in the dorsolateral striatum, restricted to Drd1+ neurons (treatment x region interaction, F(2,841) = 13.96, p < 0.0001; Bonferroni post hoc analysis, DLS naïve vs. alcohol, p = 0.0001; naïve vs. abstinence, p = 0.0001; alcohol vs. abstinence, p = 0.0591). A ~16% reduction on Chrm4 expression was observed on Drd1+ neurons in the DLS following long-term alcohol consumption, while a ~24% reduction was observed after abstinence. No differences were observed in Chrm4 expression on Drd1+ cells in the DMS or Chat+ cells in either the DMS or DLS. Data expressed as mean ± SEM; n=70-90 Chat+ and 140-150 Drd1+ cell from 5-6 rats/treatment, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.