FIG. 1.
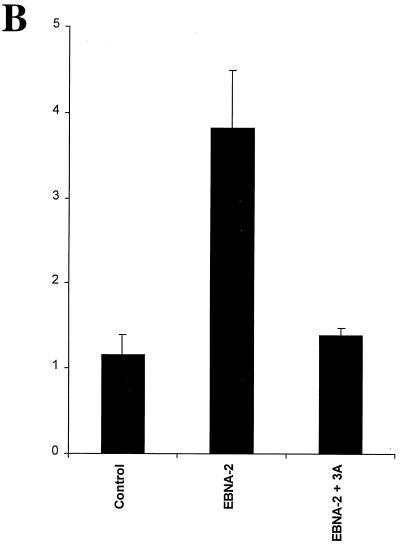
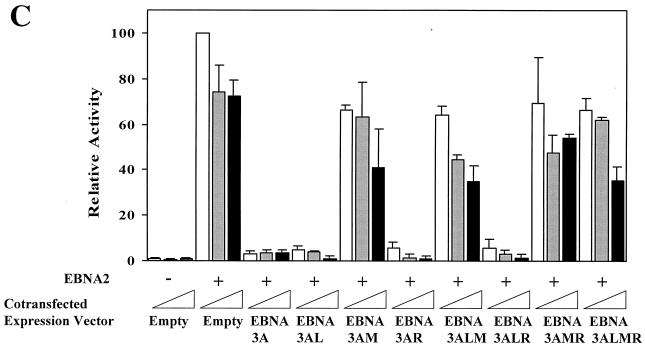
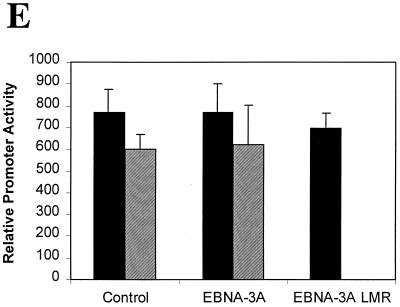
Amino acids 199, 200, and 202 are essential for functional interaction with Jκ. (A) Sequence homology among the EBNA-3 family members within the N-proximal region and mutations introduced into EBNA-3A are shown. Amino acids that were mutated are underlined. (B) EBNA-3A represses EBNA-2–Jκ-mediated transcription. Cells were transfected with a CD23-CAT reporter gene in the presence of EBNA-2 alone or with EBNA-3A. (C) Mutation of amino acids 199, 200, and 202 affects EBNA-3A's ability to repress EBNA-2–Jκ-mediated activation. BJAB cells were cotransfected with C10BLCAT, pCMVHGH, and pSG5-EBNA2 and with increasing amounts (2.5, 5, and 10 μg) of expression plasmids for wild-type or mutant EBNA-3A. In the controls, the empty vector pSG5 was used to maintain a constant amount of total DNA transfected. The average result and standard error of triplicate experiments are presented. (D) EBNA-3A does not affect levels of EBNA-2. Protein extracts from cells transiently transfected with EBNA-2 alone (control) or in the presence of wild-type or mutant EBNA-3A were analyzed by immunoblotting with a monoclonal antibody to EBNA-2. (E) EBNA-3A does not affect Jκ-independent transcription. Reporter genes controlled by either the histone H4 promoter (solid bars) or the EBV Qp promoter (hatched bars) were transfected into cells in the presence of wild-type or mutant EBNA-3A.