Fig. 3. SCPs can be mapped to cellular subtypes and known cardiomyopathy disease mechanisms.
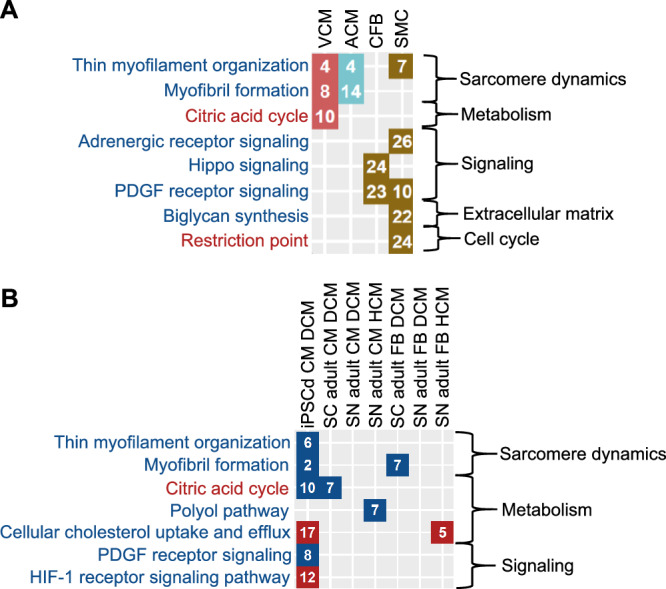
A We subjected marker genes for ventricular and atrial cardiomyocytes (VCM, red fields, and ACM, turquoise fields, respectively), cardiac fibroblasts (CFB, brown fields) and smooth muscle cells (SMC, brown fields) obtained from single nucleus RNAseq of the adult human heart29 to pathway enrichment analysis using MBCO and Fisher’s exact test. Significant SCPs of each cell type (nominal p-value ≤ 0.05) were ranked by significance (numbers in the diagram). Names of SCPs whose higher and lower activities favor a cardiotoxic response are colored red and blue, respectively. B DEGs in heart cells obtained by single cell (SC)13 or nucleus (SN)14 RNAseq from patients with DCM or HCM as well as in hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes obtained from an infant patient with DCM32 were subjected to pathway enrichment analysis using MBCO and Fisher’s exact test. Significantly up- (red fields) or downregulated (blue fields) SCPs of each cell type (nominal p-value ≤ 0.05) were ranked by significance (numbers in the diagram). Names of SCPs are colored as described in (A).
