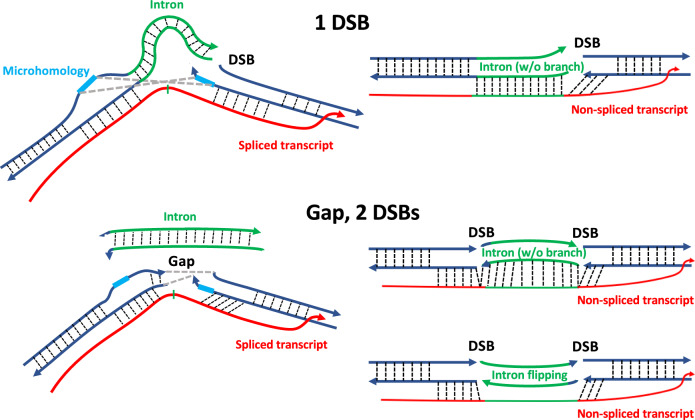
Fig. 10. Models of transcript RNA-mediated DSB repair.
When a DSB is generated near one or both exon-intron junctions of a gene, the transcript RNA of that gene supports DSB/double-strand gap repair with intron pop-out if spliced (schemes on the left), or intron retention if non-spliced (schemes on the right). On the other hand, the non-spliced transcript RNA by interacting with the DSB ends of a double-strand gap on both sides of the intron, maintains the double-strand gap ends distant from each other allowing intron flipping (scheme on the bottom right). Dotted lines, hydrogen bonds; blue lines, exon sequences; green lines, intron sequences in DNA or RNA; red line, the gene RNA transcript; thin green mark, splice site of the intron in RNA; light blue lines, microhomology; gray dashed lines, interaction between the broken DNA ends facilitated by the transcript RNA.