FIG. 4.
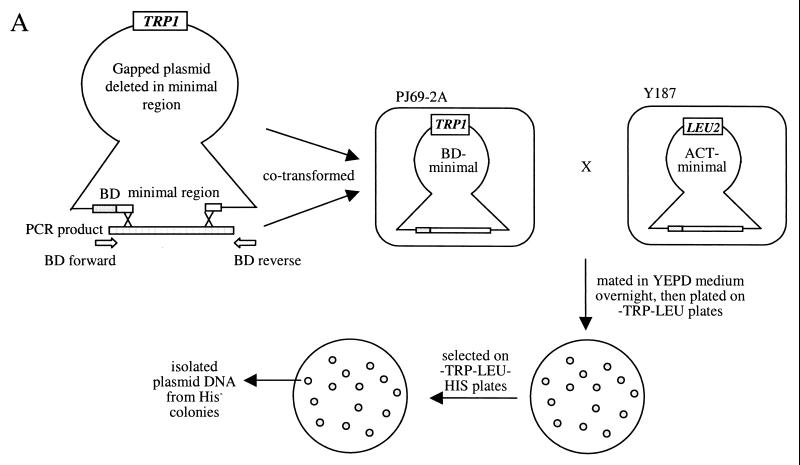
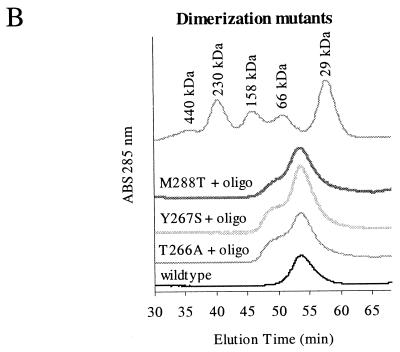
Random mutations that disrupt interaction in the minimal region. (A) Scheme showing how the screen for random mutations that disrupt helicase interaction was done. Random mutations were generated by low-fidelity PCR and recombined with a gapped plasmid in yeasts. Transformed yeasts carrying repaired plasmids were mated with a strain carrying the pACT-min plasmid, and diploids were screened for mutants that did not interact with pACT-min and were therefore His−. (B) Three of these mutants, T266A, Y267S, and M288T (see Fig. 5), were analyzed for their ability to dimerize by gel filtration. All three showed a larger monomer peak and a reduced dimer peak in the presence of an oligonucleotide. The gel filtration profile of the wild-type helicase in the absence of an oligonucleotide was included for comparison. ABS, absorbance.