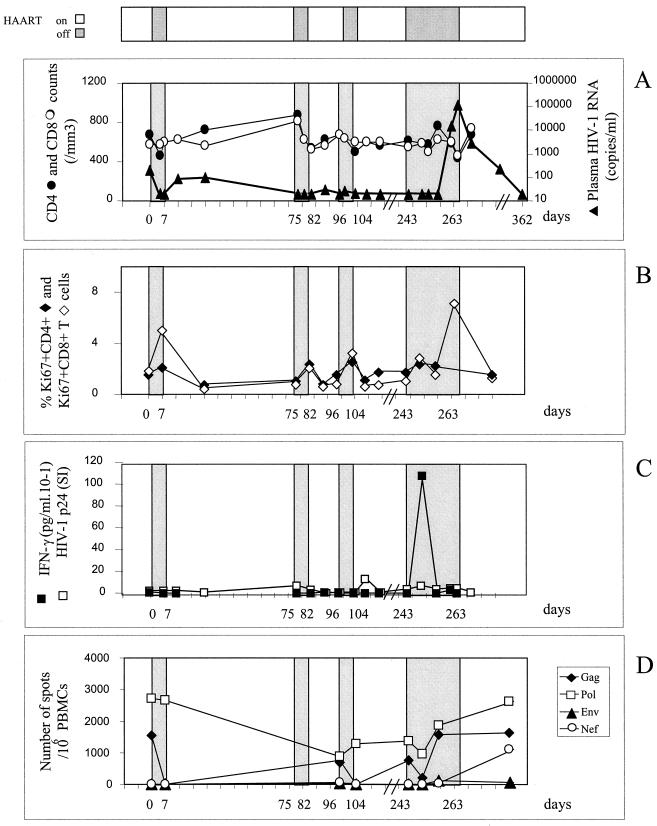
FIG. 1.
Patient 1. (A) Effect of intermittent interruptions of antiretroviral therapy on viral load and CD4 or CD8 counts. The HIV-1 RNA level was measured by RT-PCR with a limit of sensitivity of 20 copies per ml. Viral loads are expressed as numbers of HIV-1 RNA copies per milliliter of plasma; CD4 and CD8 counts were analyzed by flow cytometry with fluorescent beads as an internal standard. The values (mean ± standard deviation) in healthy people are as follows: CD4+ cells, 858 ± 260 cells/μl of plasma; CD8+ cells, 482 ± 164/μl plasma. White areas at top of the figure indicate periods of treatment (nevirapine, stavudine, and lamivudine); interruptions are in grey and are also shown in panels A to D. (B) Effect of intermittent interruptions of antiretroviral therapy on Ki67 antigen expression. Ki67 antigen expression was analyzed in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells by flow cytometry after intracellular staining. The values in healthy people are 2.5% ± 0.6% for CD4+ Ki67+ cells and 2% ± 0.6% for CD8+ Ki67+ cells. (C) Effect of intermittent interruptions of antiretroviral therapy on T-helper cell responses to HIV-1 p24 protein. HIV-1 p24-stimulated IFN-γ production by CD8-depleted PBMC was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the 2-day culture supernatants and is expressed as 10−1 picograms per milliliter; T cell proliferative responses against HIV-1 (p24) were measured on CD8-depleted PBMC, and the results are expressed as a stimulation index. (D) Effect of intermittent interruptions of antiretroviral therapy on CD8+ cell responses to HIV-1 protein. The frequency of HIV-specific CD8+ T cells was tested by a recombinant vaccinia virus ELISPOT assay. PBMC were infected with wild-type vaccinia virus or recombinant vaccinia virus Gag, Pol, Env, or Nef, and IFN-γ-producing SFC were enumerated in an 18-h ELISPOT assay. Results are expressed as the number of IFN-γ SFC per 106 PBMC.