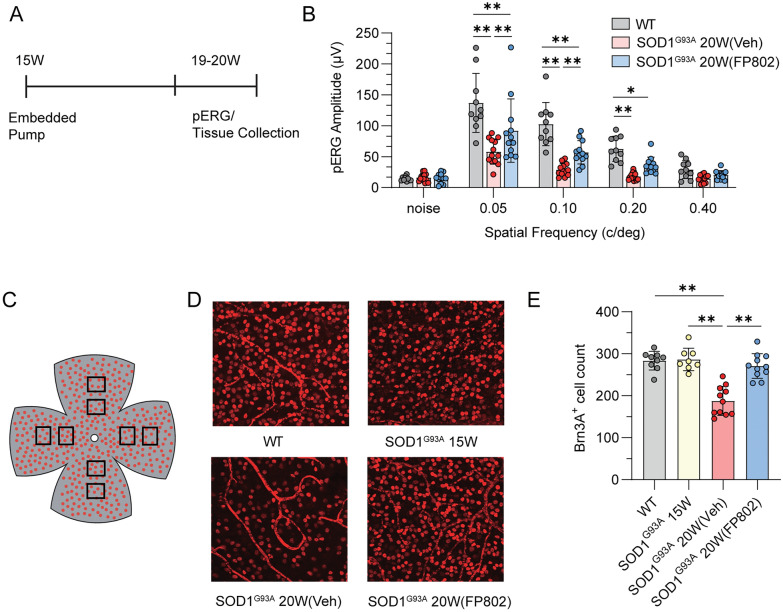
Fig. 1.
TwinF interface inhibitor FP802 protects against RGC degeneration in the SOD1G93A ALS mouse model. A Schematic of experimental protocol followed, with pump implantation (vehicle or FP802) into SOD1G93A transgenic mice from week 15, and subsequent pERG recordings and tissue collection on the same day at weeks 19–20. B Quantification of pattern-evoked ERG amplitudes (µV) measured as the amplitude of the second harmonic of the fast Fourier transformation plotted against spatial frequency of stimulation in wild-type (WT), SOD1G93A vehicle-treated and SOD1G93A FP802-treated mice at week 20 (20W). Statistical test: two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Uncorrected Fisher’s LSD for multiple comparisons. n, WT = 10; SOD1G39A 20W (Veh) = 13; SOD1G93A 20W (FP802) = 12. Individual data points represent single eyes per mouse. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. C Schematic of retinal whole-mount with squares showing the positioning of areas quantified across each quadrant. D Representative images of Brn3a immunolabelling of retinal whole-mounts from mouse groups at 15 and 20 weeks and following treatment with vehicle or FP802 as indicated. E Quantification of surviving Brn3a-positive RGCs in retinal whole-mounts (averaged across the retina as indicated in C), with cell counts given as the number of Brn3a-positive RGCs quantified per field of view (375 μm × 375 μm). Statistical test: one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. n, WT = 9; SOD1G93A 15W = 8; SOD1G93A 20W (Veh) = 11; SOD1G93A 20W (FP802) = 11. Single eyes per mouse. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01