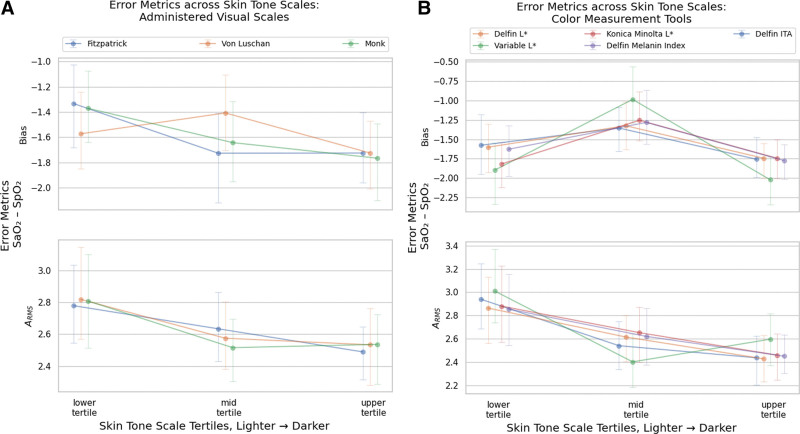
Figure 1.
Bias and accuracy root mean square (ARMS) across Skin Tone Scale tertiles. Unadjusted error metrics of Sao2–Spo2 bias and ARMS across skin tone tertiles. Tertiles are ordered from lightest to darkest, from the left to the right, under each metric. For example, for the Monk Skin Tone scale, the bias is: lightest tertile: –1.371; 95% CI, –1.646 to –1.113); mid tertile: –1.643; 95% CI, –1.890 to –1.340; darkest tertile –1.767; 95% CI, –2.038 to –1.515. Other Skin Tone Scales show similar trends, whereby the lightest tertiles present a lower Sao2–Spo2 bias. For precision and ARMS, the trends are reversed with darker tertiles presenting lower precision and ARMS. Visual representations and sensitivity analysis are shown in Supplement Figure 6 (http://links.lww.com/CCX/B379). A, Bias and ARMS in Administered Visual Scales: Monk Skin Tone, Fitzpatrick Skin Type, Von Luschan. B, Bias and ARMS in Color Measurement Tools. ITA = individual typology angle.