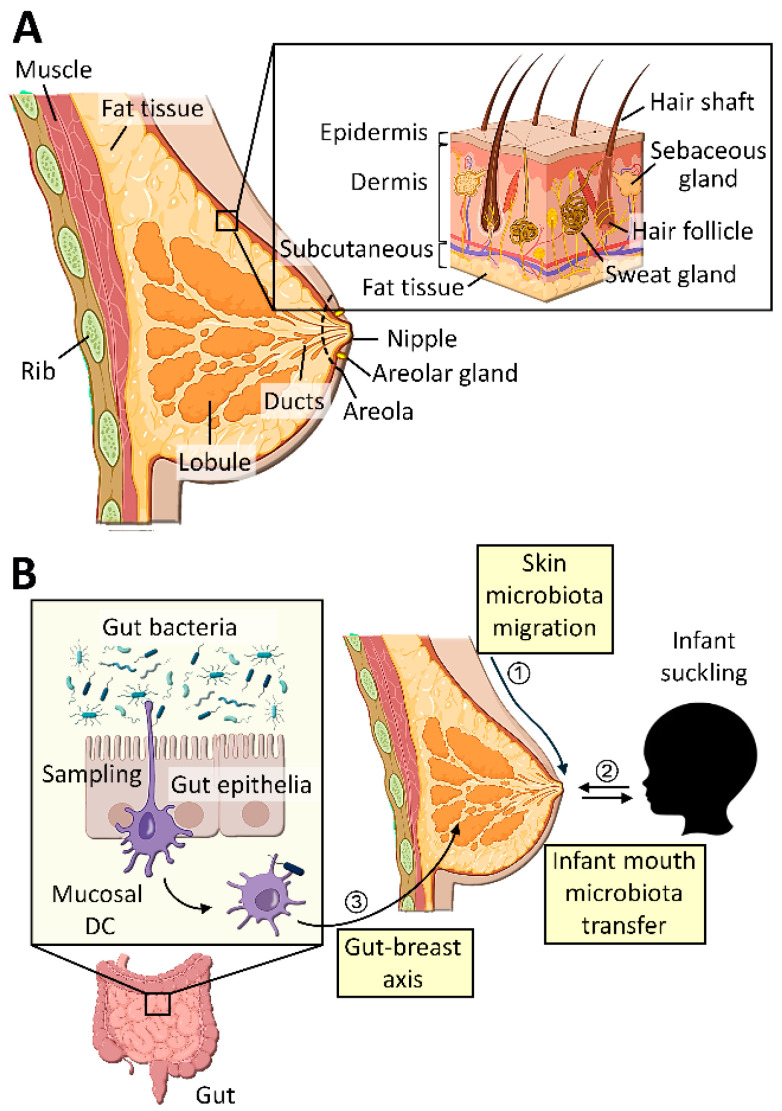
Figure 1.
Potential origins of breast tissue/milk microbiota. (A) The structure of the human breast. Inset: the structure of the skin. (B) Three potential routes of microbial transfer to the breast milk/tissue. (1) Breast skin microbiota migration. Microbes of the adjacent skin could enter the mammary gland through the areola. (2) Infant mouth microbiota transfer. During suckling, the oral microbes of the infant could enter the mammary gland through retrograde transfer. (3) Gut–breast axis. Gut mucosal dendritic cells (DCs) occasionally sample commensal bacteria in the lumen and transfer them to lymphoid tissues and eventually reach the mammary gland.