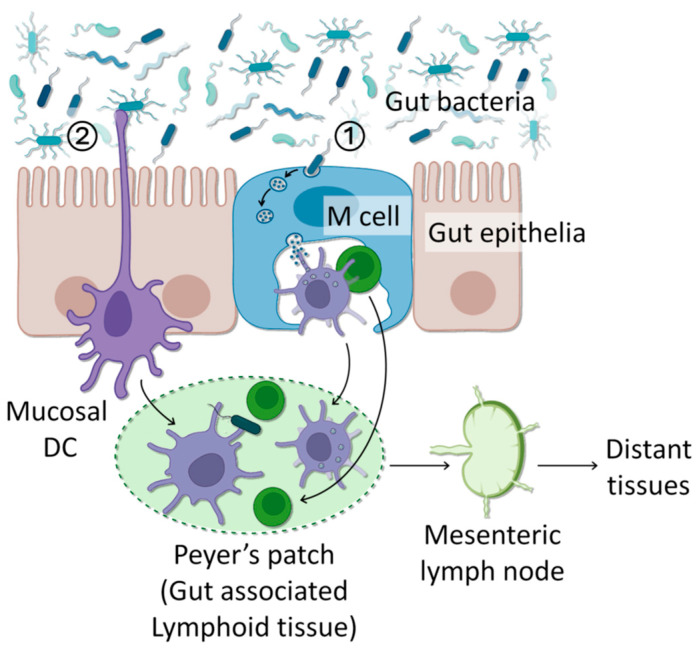
Figure 2.
Two major modes of bacterial translocation. (1) Luminal bacteria are internalized by specialized microfold (M) cells present in the gut epithelial layer. These bacteria are transcytosed and made available to mucosal immune cells. (2) Luminal bacteria are directly taken up by CD18+ phagocytic cells in the mucosal layer that penetrate the gut epithelial layer. These immune cells which have taken up bacteria migrate to gut-associated lymphoid tissues (GALTs) and then mesenteric lymph nodes, where they stay until they are disseminated to thymus, spleen, and other distant tissues.