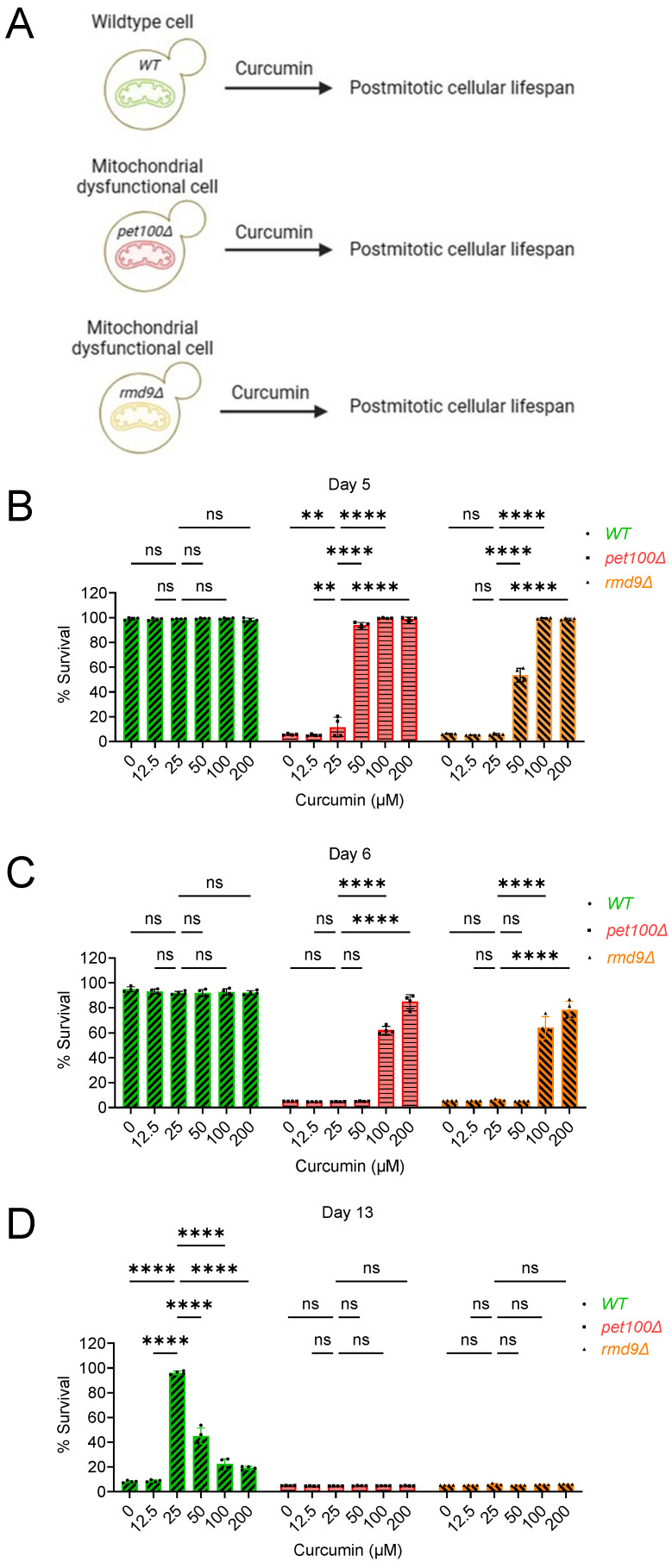
Figure 2.
Curcumin prolongs the postmitotic cellular lifespan of mitochondrial dysfunctional cells during chronological aging in yeast. (A) Schematic of the study workflow. The effect of curcumin treatment on the postmitotic cellular lifespan (PoMiCL) of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic background CEN.PK113-7D wildtype and mitochondrial-dysfunction mutants (pet100∆ and rmd9∆) was evaluated in an SD medium using a 96-well plate. Cells were incubated with indicated concentrations of curcumin in the 96-well plate. The survival of chronological aging postmitotic cells was measured on (B) day 5, (C) day 6, and (D) day 13, relative to the outgrowth of day 3. The data are presented for replicates (n = 4). Statistical significance was determined as follows: ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001 and ns (non-significant), based on a two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test.