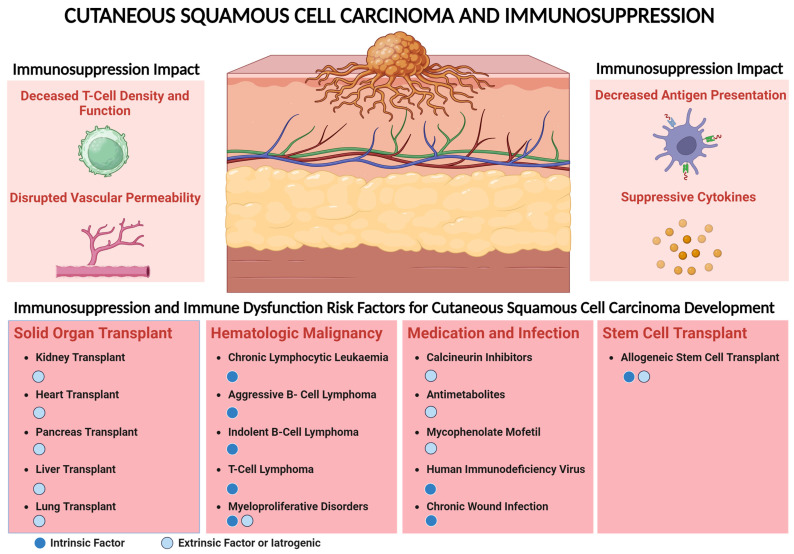
Figure 1.
Immunosuppression impact and risk factors associated with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC). Use of immunosuppressive medication such as calcineurin inhibitors, antimetabolites, and HIV infection are associated with higher risk of CSCC. Immune dysregulation can lead to decreased effector T-cell density and function and disruption of antigen-presenting mechanisms. Suppressive cytokines in chronic inflammation and patients with a history of transplant and decreased permeability of effector immune cells into the tumor can promote CSCC progression. This risk leading to CSCC development could be either intrinsic, e.g., because of modulation of the host immune system due to transplant or hematologic malignancy targeting specific immune cells, or due to extrinsic factors, e.g., the use of immunosuppressive medication including patients with transplant to prevent allograft rejection.