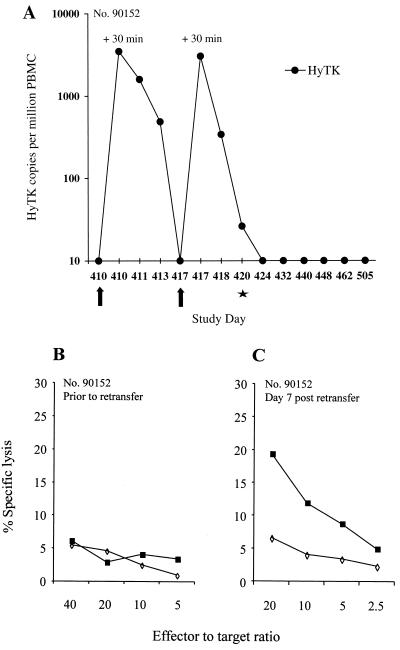
FIG. 7.
HyTK-specific CTL are elicited following readministration of HyTK-modified T cells to macaque 90152. (A) In vivo persistence of HyTK-modified T cells. Samples of PBMC collected before and on the indicated days after infusion were evaluated by real-time PCR for the frequency of HyTK sequences. Arrows indicate the days of T-cell infusions, and the star denotes an inguinal lymph node biopsy. (B and C) CTL responses specific for target antigens derived from HyTK in samples of PBMC collected before (study day 389) (B) and 7 days after (study day 417) (C) infusion. PBMC were cocultured with autologous γ-irradiated HyTK-expressing T cells and then assayed for HyTK-specific cytolytic activity against target cells, either parental (◊) or transduced to express the HyTK gene (■).