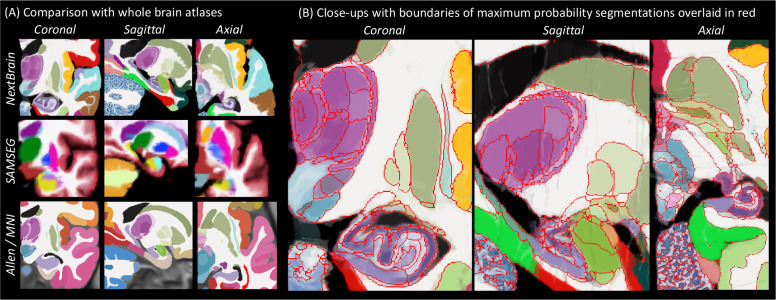
Fig. 4:
NextBrain probabilistic atlas. (A) Portions of the NextBrain probabilistic atlas (which has 333 ROIs), the SAMSEG atlas in FreeSurfer [2] (13 ROIs), and the manual labels of MNI based on the Allen atlas [7] (138 ROIs). (B) Close-up of three orthogonal slices of NextBrain. The colour coding follows the convention of the Allen atlas [7], where the hue indicates the structure (e.g., purple is thalamus, violet is hippocampus, green is amygdala) and the saturation is proportional to neuronal density. The colour of each voxel is a weighted sum of the colour corresponding to the ROIs, weighted by the corresponding probabilities at that voxel. The red lines separate ROIs based on the most probable label at each voxel, thus highlighting boundaries between ROIs of similar colour; we note that the jagged boundaries are a common discretization artefact of probabilistic atlases in regions where two or more labels mix continuously, e.g., the two layers of the cerebellar cortex.