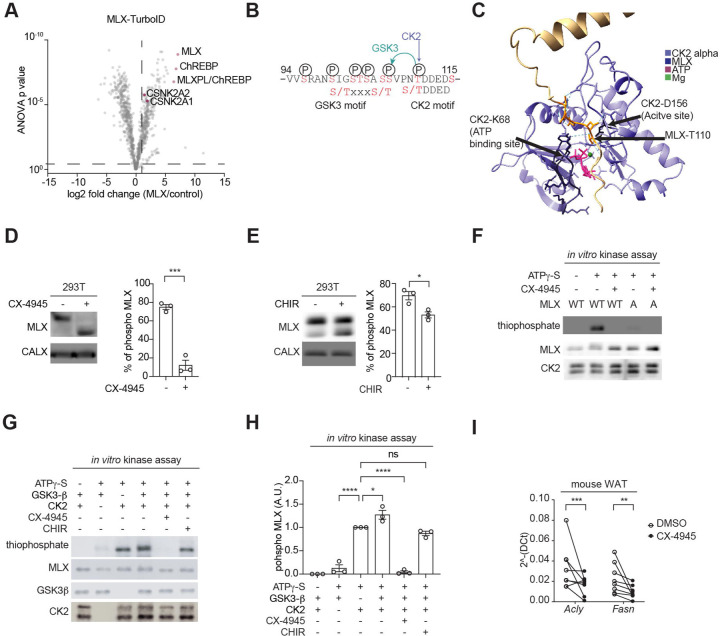
Fig. 4. Identification of CK2 and GSK3 as MLX kinases.
a. Interactors of TurboID-tagged MLX. 293T cells expressing ChREBP, HK2, and MLX-TurboID were labeled with 25 nM biotin for 10 min. N=4.
b. Putative CK2 and GSK3 phosphorylation motifs on MLX.
c. Interaction of MLX and CK2 catalytic site based on an AlphaFold3 structure prediction.
d. MLX phosphorylation in 293T cells treated with or without the CK2 inhibitor CX-4945 (10 µM) for 60 min. CALX serves as a loading control. t-test, ***p<0.001. N=3.
e. MLX phosphorylation in 293T cells treated with or without the GSK3 inhibitor CHIR99021 (5 µM) for 90 min. t-test, *p<0.05. N=3.
f. In vitro CK2-mediated MLX phosphorylation (thiophosphate). Recombinant CK2, MLX-WT or -A, and ATPg-S were incubated with or without 25 nM CX-4945 for 30 min. N=3.
g-h. In vitro CK2 and GSK3-mediated MLX phosphorylation (thiophosphate). Recombinant CK2, GSK3, MLX-WT, and ATPg-S were incubated with or without 25 nM CX-4945 or 5 µM CHIR99021 for 30 min. One-way ANOVA, *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001, ns=not significant. N=3.
i. Acly and Fasn mRNA levels in mouse WAT explants treated with 10 µM CX-4945 for 60 min. t-test, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. n=5.