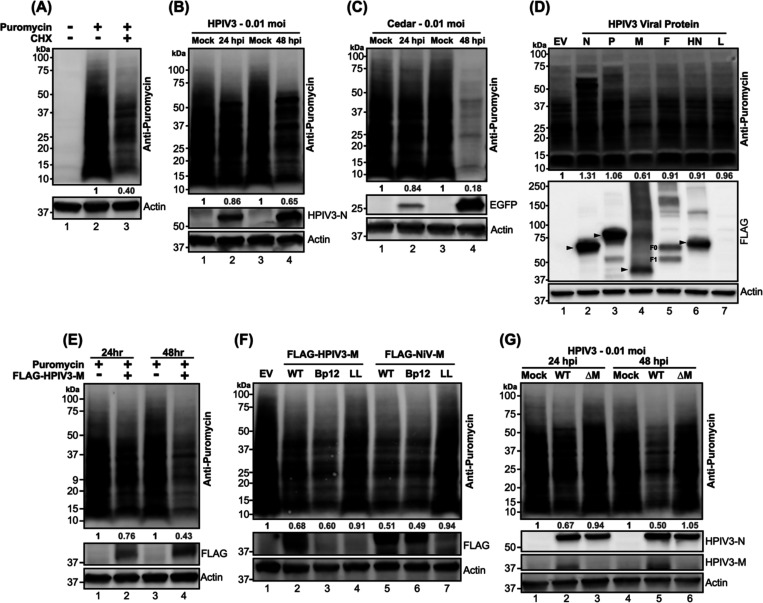
Figure 1. Puromycylation of newly synthesized protein in paramyxovirus-infected or viral proteins transfected HEK-293T cells.
(A) HEK-293Ts were treated with either mock or cycloheximide (CHX) at 200 μg/ml for 5 hours, followed by a 20-minute treatment with either mock or puromycin at 10 μg/ml. After the puromycin pulse, cells were washed with PBS and re-fed with complete media. Lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting, and newly synthesized (puromycylated) proteins were probed using an anti-puromycin antibody. (B-C) HEK-293Ts were inoculated with mock, HPIV3, or Cedar virus and puromycin pulsed at indicated time points. Lysates were immunoblotted to probe puromycylated proteins. The expression of HPIV3 nucleocapsid (N) and EGFP served as controls for HPIV3 and Cedar infections, respectively. (D) Flag-fused viral proteins from individual HPIV3 genes or an empty vector (EV) were expressed in HEK-293T cells for 48 hours, followed by puromycylation and immunoblot analysis to detect puromycylated proteins. Expression of viral proteins was detected with an anti-FLAG antibody, with molecular weights indicated by black arrows. F0: F precursor. F1: cleaved F. (E-F) HEK-293T cells were expressed designated FLAG-fused matrix (M) proteins from HPIV3 or NiV, including wild-type (WT) and mutants (Bp12: NLS mutant, LL: NES mutant), along with EV control for 24 or 48 hrs. Following puromycylation, immunoblotting was conducted to determine the puromycylated protein and flag-fused matrix. (G) HPIV3 or HPIV3ΔM virus-infected HEK-293Ts were analyzed by immunoblotting after puromycylation at 24- and 48-hrs post-infection to detect puromycylated protein and HPIV3 viral proteins. HPIVP3-N and HPIV3-M served as infection control. The numbers below each column indicate the relative protein abundance measured by densitometry and normalized as described in the Materials and Methods.