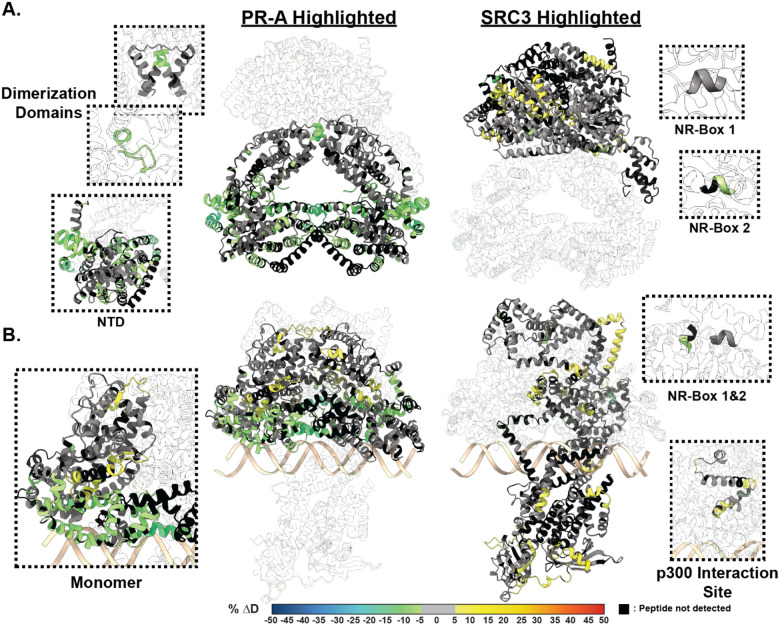
Figure 3. SRC3 induces LBD changes to PR upon PRE addition.
A. Left HDX overlay (PR-A vs. PR-A:SRC3) mapped onto AlphaFold3.0 model of the PR-A:SRC3 ternary complex with the PR homodimer highlighted. Zoomed-in sections of PR corresponding to the dimerization domains (Amino acids: 720–769 and 438–454) and N-terminal domain (PR-A amino acids 1–476) highlighted with matching HDX overlays. Right. Differential HDX overlay of SRC3 vs. PR-A:SRC3 onto the best scoring PR:SRC3 apo complex with SRC3 highlighted. NR-Boxes 1 and 2 (amino acids 685–689 and 738–742, respectively) blown up to show differential exchange. B. Left HDX overlay (PR-A:PRE vs. PR-A:SRC3:PRE) mapped onto AlphFold3.0 model of PR-A:SRC3:PRE ternary complex with the PR homodimer highlighted. One PR-A monomer is shown as a zoomed-in section. Right. Differential HDX overlay of SRC3 vs. PR-A:SRC3:PRE onto the best scoring PR:SRC3 apo complex with SRC3 highlighted. NR-Boxes 1 and 2 and the p300 interaction site (amino acids 1023–1093) are highlighted to show differential exchange. Black peptide regions correspond to peptides not identified by HDX-MS. Each color represents the percent change in deuterium incorporation (Δ%D), following the scale shown at the bottom.