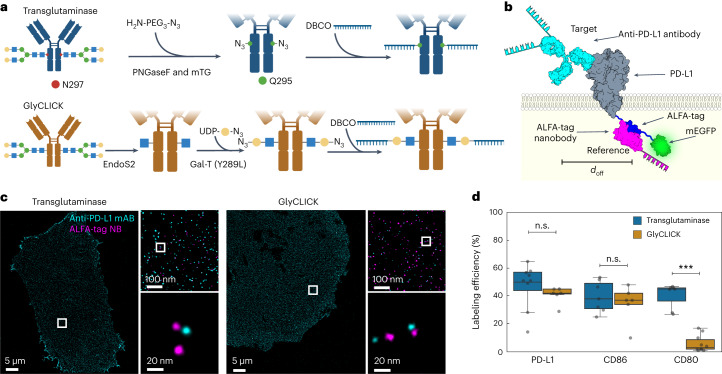
Fig. 2. Labeling efficiency evaluation of antibody conjugation methods.
a, Schematics of antibody–DNA conjugation via PNGase/transglutaminase or GlyCLICK. For both, conjugation occurs at the N-glycan Fc part of the antibody yielding 1 or 2 DNA strands per antibody. b, Illustration of labeling efficiency determination for target anti-PD-L1 antibody (cyan). For antibody characterization, ALFA-tag was inserted at the PD-L1 C-terminus, while mEGFP served as an expression indicator. Colocalization of target and reference signal (magenta) revealed underlying labeling efficiency. c, Two-plex Exchange-PAINT image of CHO PD-L1–ALFA–mEGFP cells. Zoom-ins depict target anti-PD-L1 antibody colocalizing with respective ALFA-tag nanobody. d, Fitting the NND data to a two-population model reveals the labeling efficiency of three different target antibodies. Data are shown as a box plot, where the median is indicated by the center black line. Boxes extend from the 25th to the 75th percentile of each group’s distribution of values. The whiskers extend to points that lie within 1.5 interquantile range of the lower and upper quartile. Data are of n = 9 (PD-L1 and transglutaminase), n = 7 (PD-L1 and GlyCLICK, CD80 and transglutaminase, and CD86 and transglutaminase), n = 10 (CD80 and GlyCLICK) and n = 5 (CD86 and GlyCLICK) cells over three independent experiments and was tested for statistical significance via a two-sided bootstrap ratio test. ***P < 0.001, n.s., non-significant.