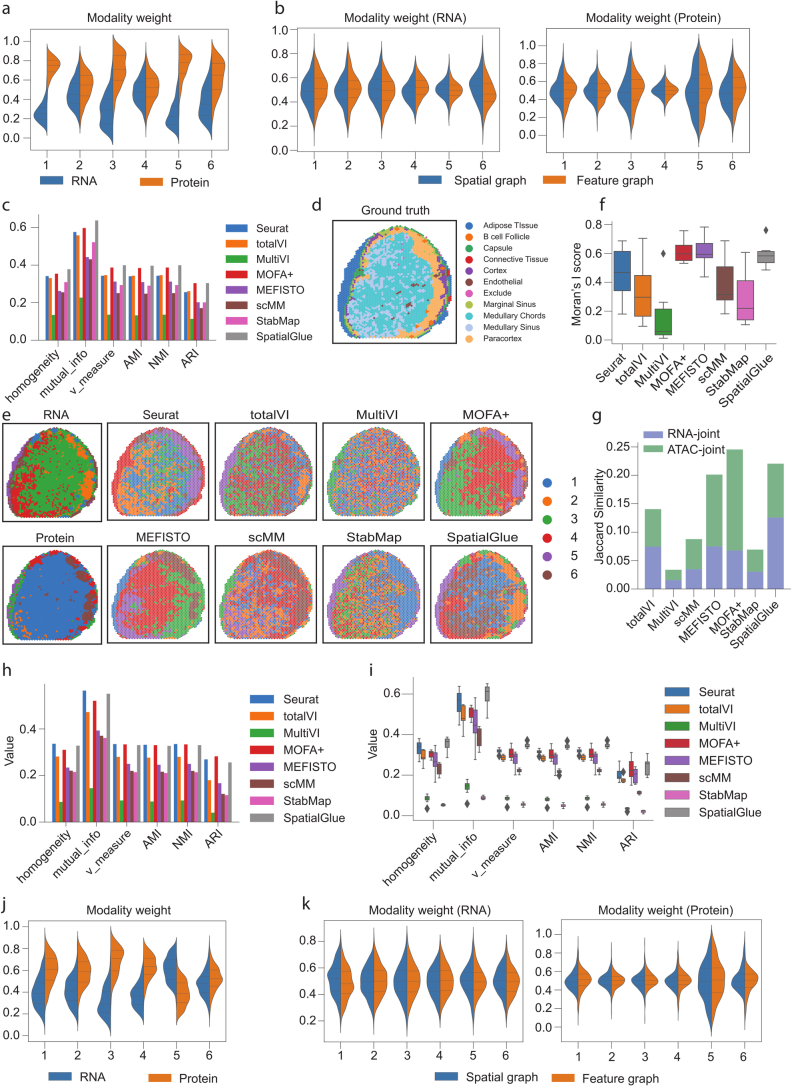
Extended Data Fig. 3. Results for lymph node samples A1 (a-c) and D1(d-k).
(a) SpatialGlue’s between-modality weight explaining the importance of each modality to each cluster for the lymph node A1 sample. (b) Within-modality weights for the RNA and protein modalities explaining the contributions of the spatial and feature graphs to each cluster. (c) Quantitative evaluation of SpatialGlue and competing methods. (d) Ground truth for the lymph node D1 sample. (e) Spatial plots of RNA and protein data (left), and clustering results of single-cell and spatial multi-omics methods, Seurat, totalVI, MultiVI, MOFA+, MEFISTO, scMM, StabMap, and SpatialGlue. (f) Comparison of Moran’s I score. In the box plot, the center line denotes the median, box limits denote the upper and lower quartiles, and whiskers denote the 1.5× interquartile range. n = 6 clusters. (g) Comparison of Jaccard Similarity scores. (h) Quantitative evaluation with six supervised metrics. (i) Box plots of six supervised metrics for clustering results with number of clusters ranging from 4 to 11. In the box plot, the center line denotes the median, box limits denote the upper and lower quartiles, and whiskers denote the 1.5× interquartile range. n = 8 clustering results with different resolutions for each method. (j) Between-modality weights explaining the importance of each modality to each cluster. (k) Within-modality weights for the RNA and protein modalities explaining the contributions of the spatial and feature graphs to each cluster.