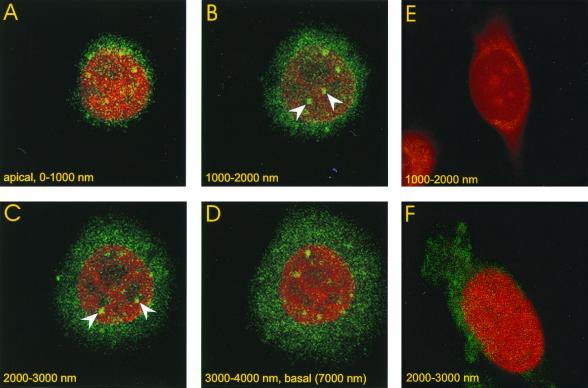
FIG. 8.
Detection of the major capsid protein in the nuclei of Pk1 cells by immune fluorescence. Pk1 cells were seeded on glass chamber slides (104/cm2) in the presence of aphidicolin. The cells were infected with GFP-bac after 12 h at an MOI of 500 for 30 min, followed by a wash, as in Fig. 4 and 7. Cells were fixed 4 h after infection and analyzed by immune fluorescence using an antibody against the major capsid protein p39 as described in Materials and Methods. Four successive, apical- to basal-side confocal images are shown, each 1 μm thick. Spots of green fluorescence indicate the presence of viral capsids in the nucleus, which is stained red with propidium bromide. Nuclear spots not visible in adjacent sections, which establishes their nuclear localization, are marked with arrows. (E) Confocal section, 1 μm, of infected cell treated with secondary antibody only. (F) Confocal section, 1 μm, of uninfected cell treated with primary and secondary antibody.