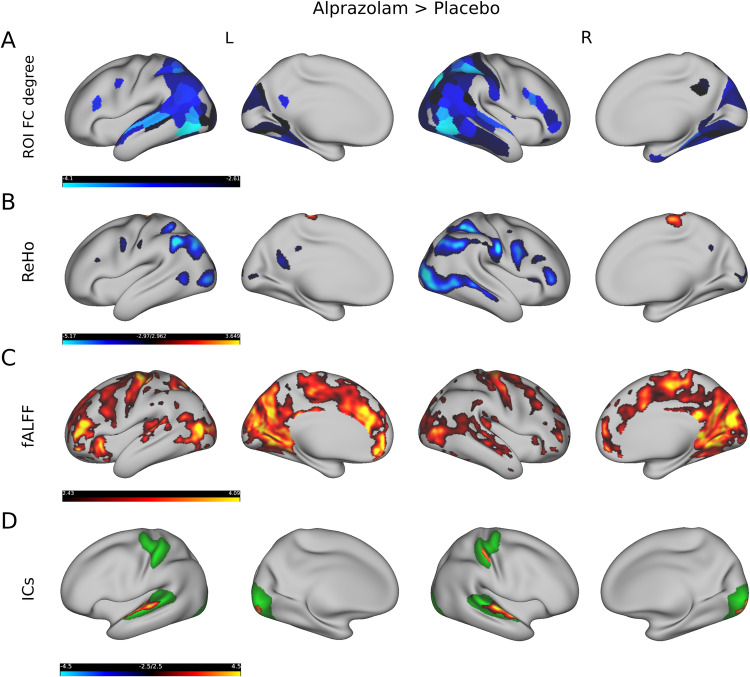
Fig. 4. Comparison of rs-fMRI measures between alprazolam and placebo.
The first row (A) shows the regions in the left (L) and right (R) hemisphere where FC degree was significantly lower after administering alprazolam compared to placebo. The second row (B) depicts several regions in which local connectivity, as defined by ReHo, was lower after administering alprazolam compared to placebo, except for one region in superior/medial aspects of somato-motor cortex. The third row (C) shows that low-frequency amplitudes, as derived from fALFF, were higher after administering alprazolam compared to placebo. The fourth row (D) illustrates alterations in ICA-based resting-state networks, which display higher connectivity after the administration of alprazolam within the temporal, occipital and right somatosensory cortex. Yellow and blue colours depict t-values (from blue, alprazolam < placebo, to yellow, alprazolam > placebo).