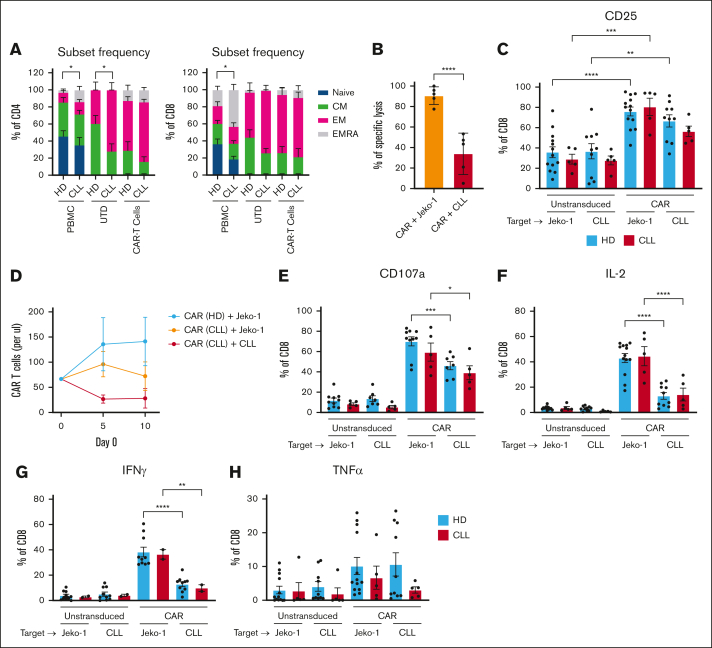
Figure 2.
Effector function of CAR T cells is reduced in presence of CLL cells. (A) A pure population of T cells were obtained from PBMCs from HDs and patients with CLL. These purified T cells were transduced with a CD19BBζ CAR construct or left untransduced (UTD) and expanded for 14 days. The phenotype of the HD and CLL (CAR) T cells was characterized before T-cell selection (PBMC) or after transduction (UTD, transduced; CAR T cells) based on CD27 and CD45RA expression as follows: naive were CD27+CD45RA+, central memory (CM) were CD27+CD45RA−, effector memory (EM) were CD27−CD45RA−, and EM RA+ (EMRA) were CD27–CD45+ (HD, n = 3-10; CLL, n = 3-6). (B) CAR T cells were cultured with either JeKo-1 or autologous CLL cells, and after 1 day, specific lysis was calculated using TO-PRO and MitoTracker Orange (CLL, n = 5). In this same experiment, (C) UTD T cells and CAR T cells were analyzed for expression of CD25. (D) In a repeated stimulation assay, CAR T cells were cocultured in a 1:1 ratio with either JeKo-1 or autologous CLL cells, which were added every 5 days, and proliferation was measured every 5 days using counting beads (HD, n = 3; CLL, n = 3). (E-H) After 1 day of CAR T cells and (autologous) CLL or JeKo-1 coculture, expression of CD107a (E), IL-2 (F), IFN-γ (G), and TNF-α (H) was measured intracellularly (HD, n = 6-13; CLL, n = 2-5). P values were calculated using a Mann-Whitney test for panel A, a paired t test for panel B, a 1-way ANOVA for panels C,E-H, or a 2-way ANOVA for panel D. The data are presented as mean ± SEM; ∗P ≤ .05, ∗∗P ≤ .01, ∗∗∗P ≤ .001, ∗∗∗∗P ≤ .0001.