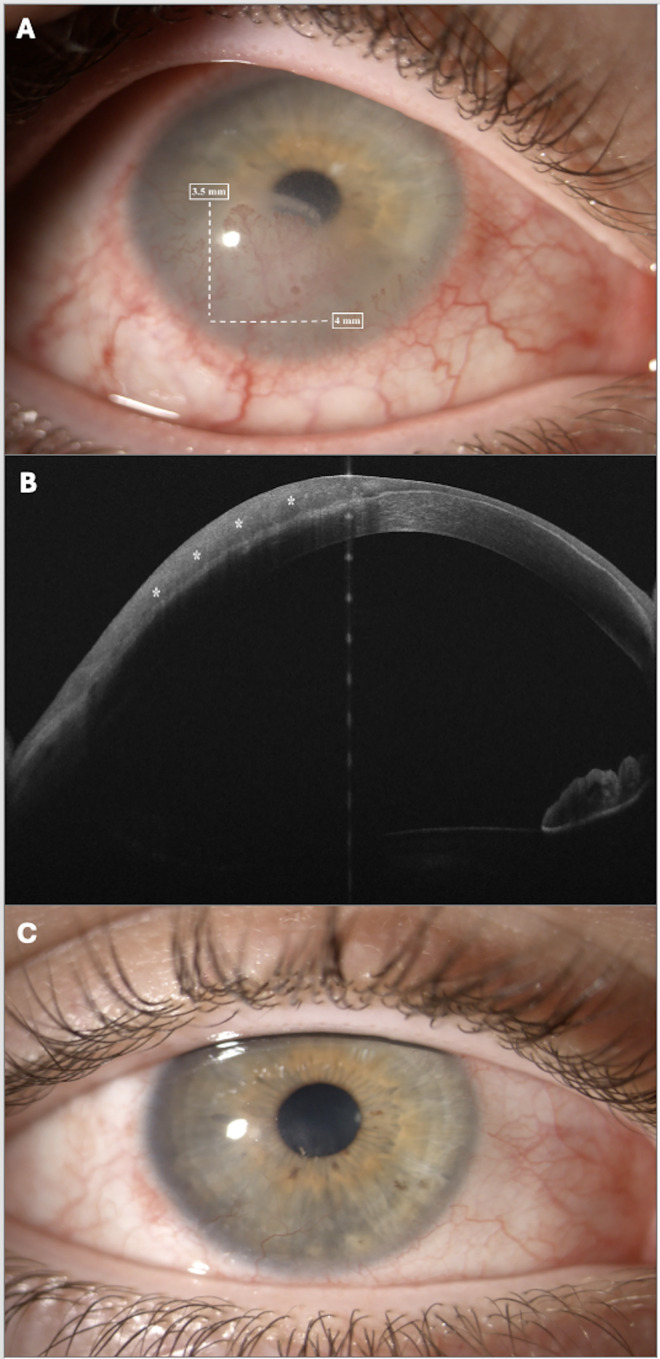
Figure 1.
(A) Slit-lamp photograph before starting interferon alfa-2b treatment. External photograph depicting in right eye an inferior corneal infiltrate with stromal neovascularization branching from a conjunctival vessel. The lesion extended at limbus for 4 mm (white arrow) and 3.5 mm into cornea (white arrow). (B) Anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT) findings. AS-OCT illustrated the abnormal hyper-reflective region (asterisk) suggestive of ocular surface squamous neoplasia. The lesion extended for about 50% of corneal depth. (C) Slit-lamp photograph after six months of interferon alfa-2b treatment. External photograph after 6 months of interferon alfa-2b treatment. The corneal infiltrate improved dramatically with regression of neovascularization and restored corneal transparency.