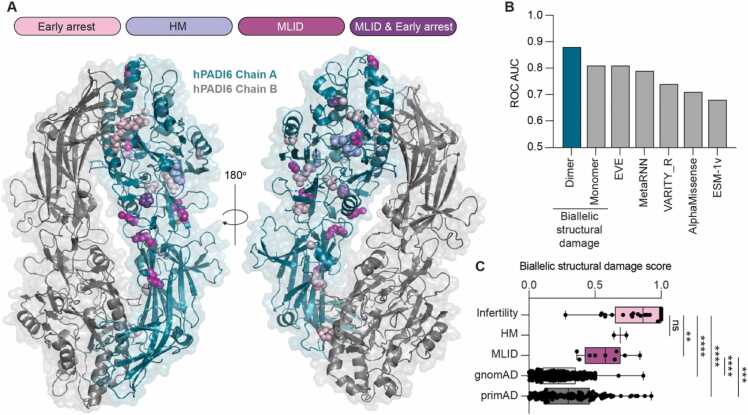
Fig. 6.
Structural damage explains clinically significant hPADI6 variants. (A) hPADI6 dimer structure with clinically significant hPADI6 variants highlighted on Chain A as spheres. Variants that result in early embryonic developmental arrest shown in light pink, hydatidiform moles in lilac, multi-locus imprinting disorders (MLID) in offspring in magenta, and variants that have been reported to result in both MLID and early embryonic developmental arrest in purple. (B) Performance of biallelic damage scores, calculated from the dimeric and monomeric structures, as well as from five sequence-based variant effect predictors, at discriminating between infertility and MLID patients, as measured by ROC AUC, whereby a value of 1 indicates perfect discrimination, and 0.5 would be expected for random chance. (C) Distribution of biallelic structural damage scores, calculated from the full dimer structure, for women with variants associated with infertility, HM and MLID, as well as putatively unaffected controls from gnomAD and primAD.