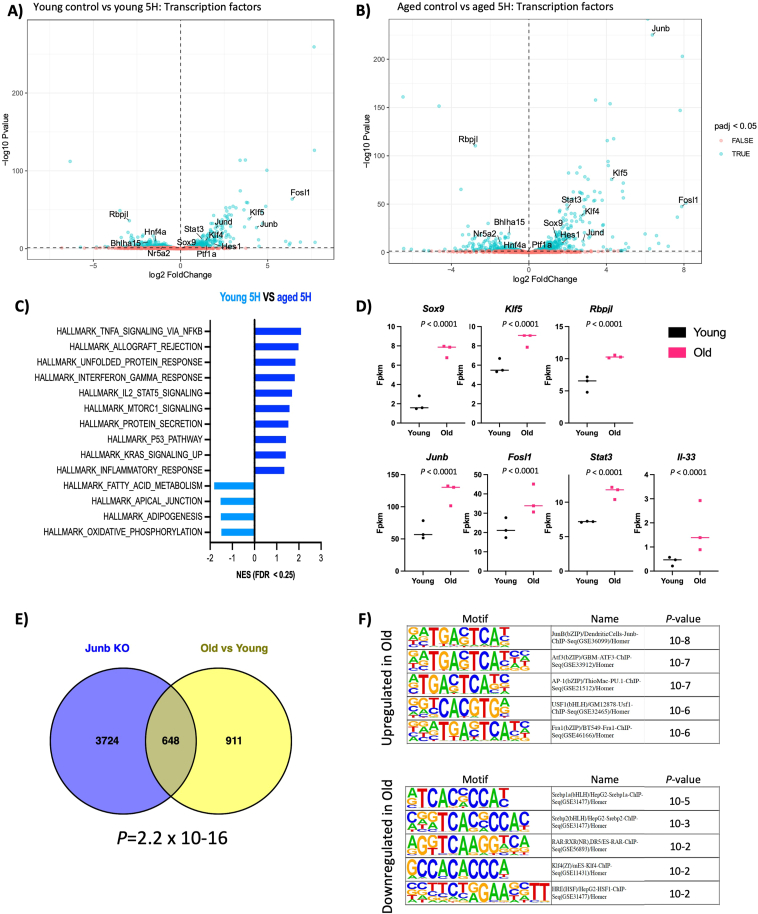
Figure 6.
Acinar cells show a proinflammatory response to injury in aged mice. (A and B) Volcano plots showing statistical significance (−log10 P value) on the y-axis versus magnitude of fold change (log2 FC) on the x-axis. Each dot represents a gene. The genes are color-coded by adjusted P value (padj) < 0.05 (blue) and > 0.05 (red). (C) Gene set enrichment analysis of hallmark signatures gene sets between 5H old and young mice. Significantly enriched hallmark signature gene sets were determined by FDR q-value < 0.25 and nominal P value < .05. (D) Differential gene expression analysis of selected genes as determined by RNAseq and DESEq2 analysis comparing old and young mice at the 5H time point. We observed upregulation of markers of pancreas development and proinflammatory signals in old mice compared to young. n = 3 mice/group. (E) Venn diagram depicting the overlap between the following datasets. Junb KO: differentially expressed genes in Junb KO vs WT control cell line derived from an autochthonous model of PDAC. Old vs Young: differentially expressed genes in old and young mice at the 5H time point. (F) We analyzed the transcription factor binding sites in the promoter region of differentially expressed genes in old and young mice at the 5H time point by HOMER. The binding site for Junb is the top enriched in the set of upregulated genes.