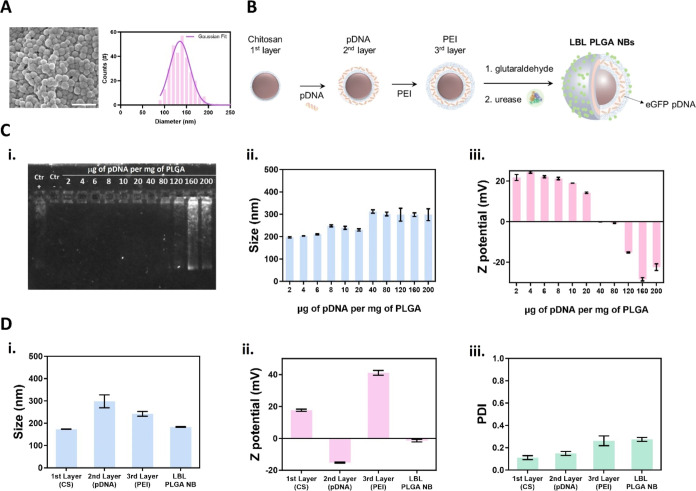
Figure 1.
Design and synthesis of layer-by-layer pDNA-loaded urease-powered PLGA nanobots (LBL PLGA NBs). (A) Representative SEM image of PLGA NPs and size distribution of PLGA NPs determined by SEM analysis of 300 NPs from 3 different synthesis. The scale bar represents 400 nm. (B) PLGA NPs coated with chitosan (1st layer) were used for electrostatic loading of the negatively charged pDNA (2nd layer), which was further functionalized with PEI (3rd layer). LBL PLGA NPs were further functionalized with glutaraldehyde to form LBL PLGA@Glu, after which they were incubated in the presence of urease to finally form LBL PLGA NBs. (C) (i) Agarose gel of the supernatants collected from centrifugation and the physicochemical characterization of the pDNA loaded PLGA NPs by (i) dynamic light scattering and (ii) ζ-potential analysis after loading different pDNA/PLGA NPs mass ratios. (D) Physicochemical characterization of final LBL PLGA NBs and the different synthetic steps by (i) dynamic light scattering, (ii) ζ-potential analysis, and (iii) PDI.