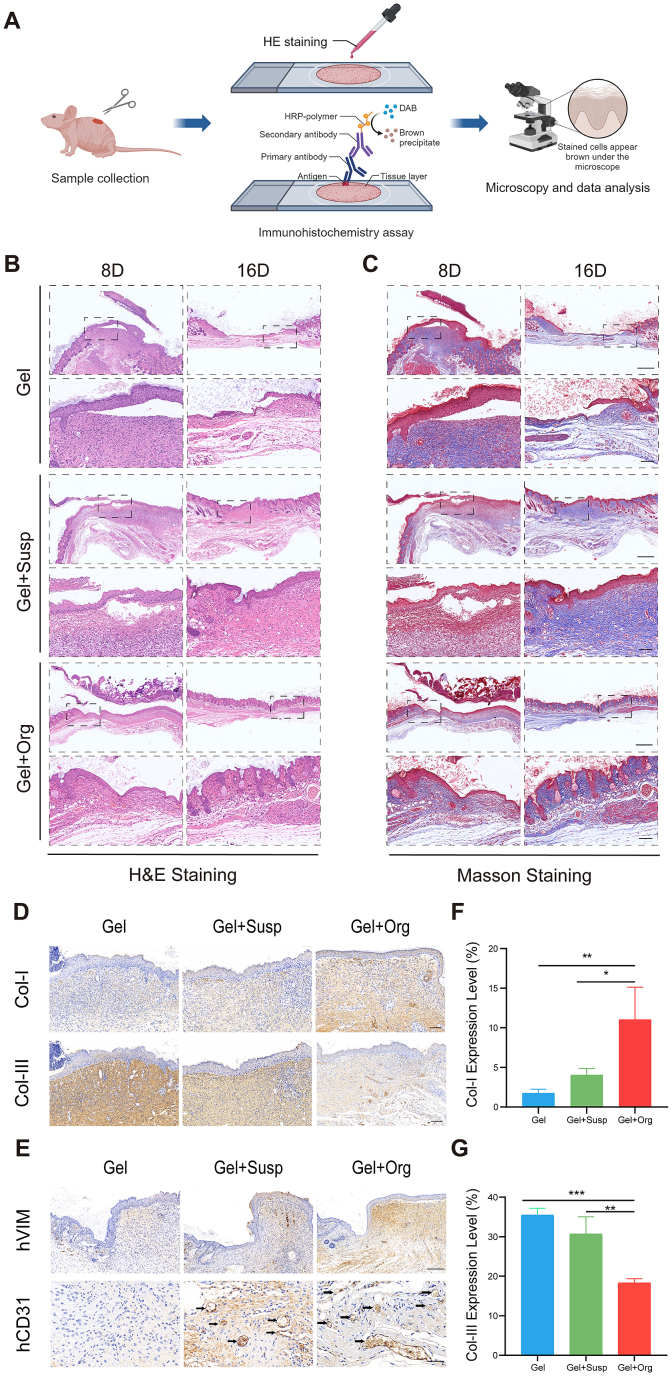
Fig. 6.
3D bioprinting skin organoid repairs and improves quality of wound healing through in-situ replacement. (A) The histopathological staining were proceeded to evaluate the quality of wound-healing. (B) H&E staining of the wound indicated the healing condition at 8 and 16 days. (C) Masson's staining of the wound sections at day 8 and day 16. Scale bar = 500 μm(Top). Scale bar = 100 μm(Bottom). (D) Immunohistochemical images of wound tissues stained by Col-I and Col-III (brown) on days 16, respectively. Scale bar = 100 μm. (E) Immunohistochemical images of wound tissues stained by human specific VIM and CD31 (brown) on days 16, respectively. Scale bar = 200 μm(Top). Scale bar = 50 μm(Bottom). (F) The quantitative analysis of Col-I, (G) Col-III of the wound sections in day 16. n = 3. Statistical significances were analyzed using t-test and one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with control group.