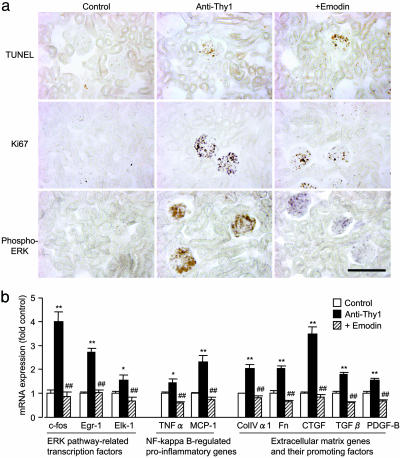
Fig. 4.
The resolution of GN by CK2 inhibition is closely associated with its antiproliferative, antiinflammatory, and antifibrotic effects. (a) TUNEL staining (Top) and immunohistochemical staining for Ki67 (Middle) and phospho-ERK (Bottom) of the renal tissue in anti-Thy1 GN rats. (Original magnification: ×120. Bar, 100 μm.) (b) Real-time PCR analysis of expression of ERK pathway related transcription factors (c-fos, Egr-1, and Elk-1), NF-κB-regulated proinflammatory genes (TNFα and MCP-1), extracellular matrix genes (collagen IVα1 and fibronectin), and their promoting factors (connective tissue growth factor, TGFβ1, and platelet-derived growth factor B) in the renal cortex of anti-Thy1 GN rats. Data are shown as mean ± SEM.; n = 5 animals. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 compared with the control group; ##, P < 0.01 compared with the anti-Thy1 group. ColIVα1, collagen IVα1; Fn, fibronectin; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; PDGF-B, platelet-derived growth factor B.