Fig. 2.
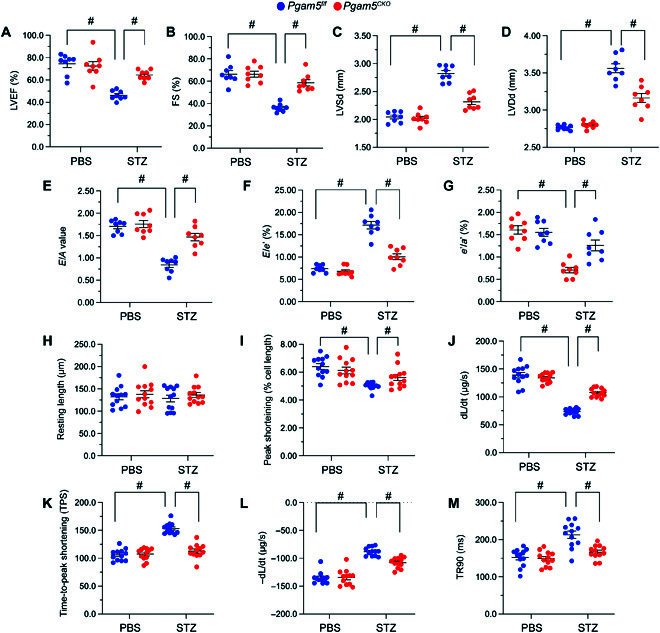
PGAM5 deficiency sustains myocardial function in diabetic mice. In vivo, the Pgam5CKO and Pgam5f/f mice were injected intraperitoneally with STZ (50 mg/kg dissolved in 0.1 mol/l of citrate buffer) for 5 consecutive days to induce diabetes. Nondiabetic mice were the age- and sex-matched, which were injected with the same volume of PBS. In vitro, cardiomyocytes were isolated from STZ-treated Pgam5CKO and Pgam5f/f mice. (A to G) Echocardiography analysis. (A) LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; (B) FS, fractional shortening; (C) LVSd, left ventricular systolic dimension; (D) LVDd, left ventricular diastolic dimension; (E) E/A, early to late (atrial) mitral flow velocity ratio; (F) E/e′, ratio of mitral peak velocity of early filling to early diastolic mitral annular velocity; and (G) e′/a′, ratio of diastolic mitral annulus velocities. (H to M) Analysis of contractile parameters in acutely isolated, single cardiomyocytes from Pgam5CKO and Pgam5f/f mice. (H) Resting length in cardiomyocytes; (I) PS, peaking shortening; (J) +dL/dt, maximal velocity of shortening; (K) TPS, time-to-peak shortening; (L) −dL/dt, maximal velocity of relengthening; and (M) TR90, time-to-90% relengthening. Values are presented as mean ± SEM. For in vivo data, n = 6 mice per group. For in vitro experiments, n = 4 independent experiments. #P < 0.05.
