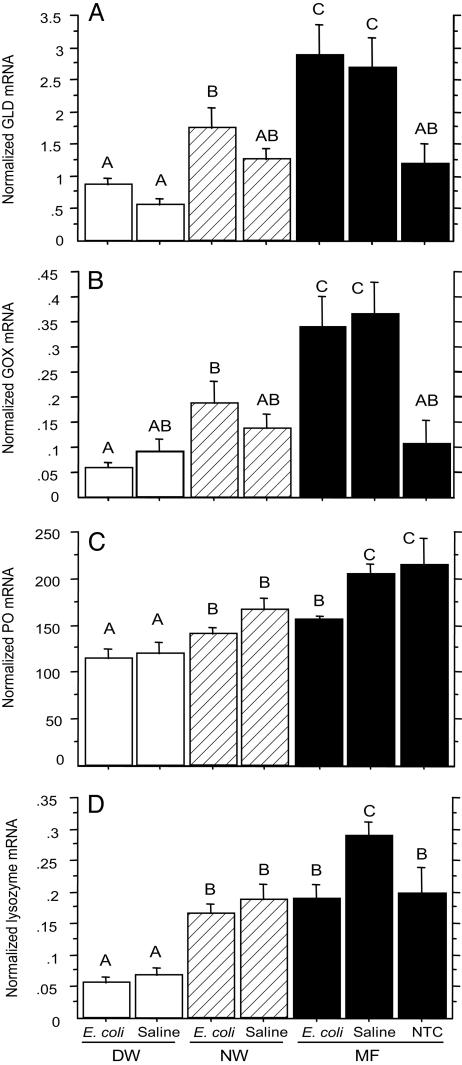
Fig. 3.
The effects of varroa infestation on the expression of genes encoding the immunity-related enzymes in newly emerged worker bees: DW, NW, and MF. The bees were either injected with bee saline or heat-killed E. coli suspended in the saline. NTC refers to the nontreatment control (i.e., the MF bees without injection). All of the values shown are mean ± SEM. (A) The expression of GLD gene was suppressed in the mite-infested bees. The bars with different letters are significantly different (ANOVA, P < 0.0001; pairwise comparison with Fisher's PLSD, P ≤ 0.0159). (B) The expression of GOX gene was suppressed in the varroa-infested bees. The bars with different letters are significantly different (ANOVA, P < 0.0001; pairwise comparison with Fisher's PLSD, P ≤ 0.0386). (C) Varroa infestation suppressed the expression of PO gene. The bars with different letters are significantly different (ANOVA, P < 0.0001; pairwise comparison with Fisher's PLSD, P ≤ 0.0495). (D) Varroa infestation suppressed the expression of lysozyme gene. The bars with different letters are significantly different (ANOVA, P < 0.0001; pairwise comparison with Fisher's PLSD, P ≤ 0.0069).