Figure:
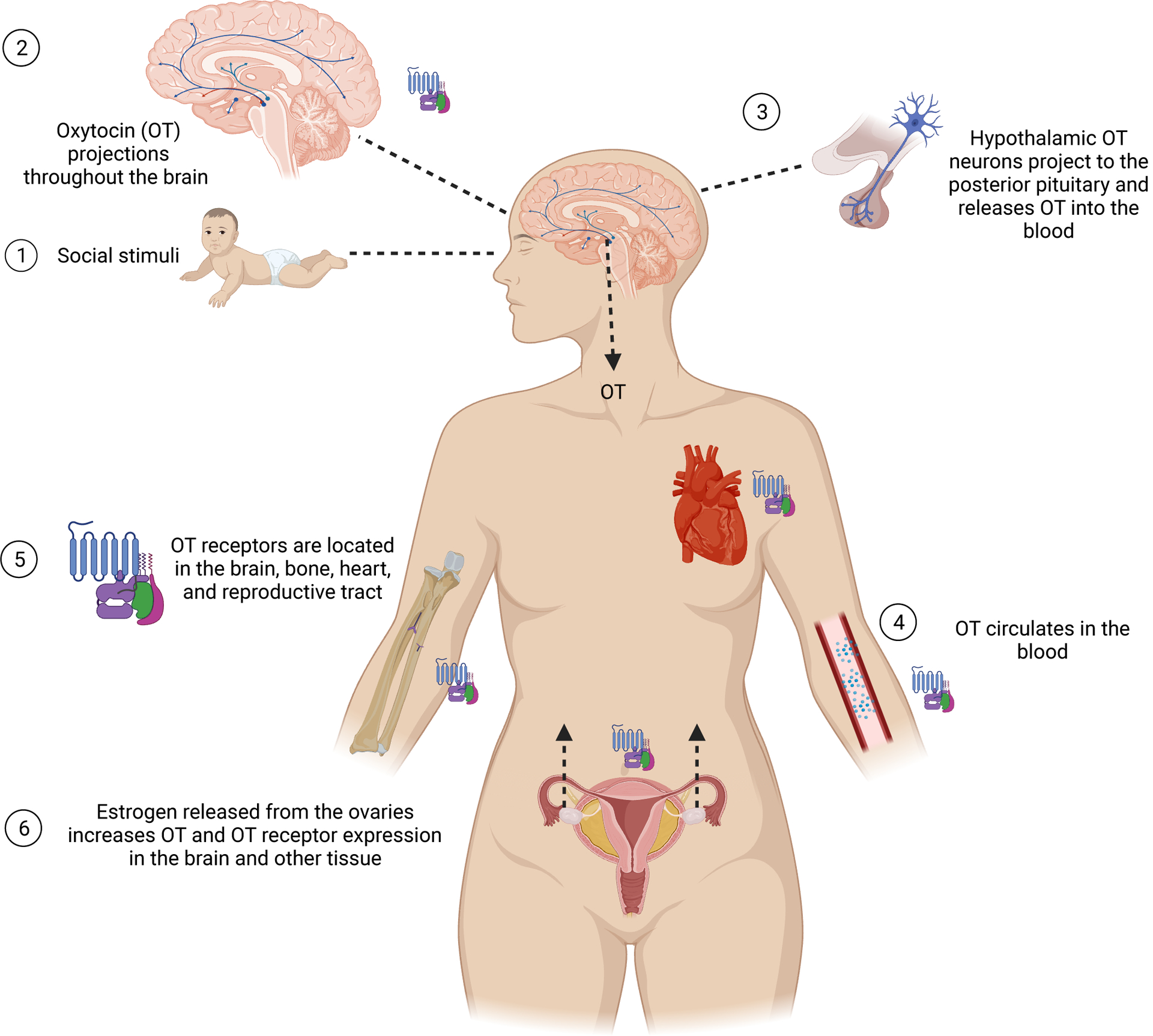
Central and peripheral release of oxytocin and its function in women’s body. (Created with BioRender.com)
1. Social experiences such interacting with loved ones causes oxytocin (OT) release in the hypothalamus.
2. OT in the brain regulates social behaviors via OT projections from the hypothalamus to emotional, reward and memory-related brain regions such as the amygdala, hippocampus, local projections to the hypothalamus, and nucleus accumbens.
3. Hypothalamic OT neurons project to the posterior pituitary gland and OT is released from the pituitary in a pulsatile manner into the blood.
4. OT circulates in the bloodstream and concentrations fluctuate due to pulsatile release and rapid degradation.
5. OT receptors are metabotropic G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). They are found throughout brain tissue, bone systems, the cardiovascular system, and the reproductive tract.
6. Estrogen secretion from the ovaries enhances OT activity via increasing OT and OT receptor expression throughout the brain and other tissue. Aging is accompanied by a decrease in estrogen levels and may lead to compromised OT signaling.
