Fig. 2. VC2 encodes a structurally functional tailocin.
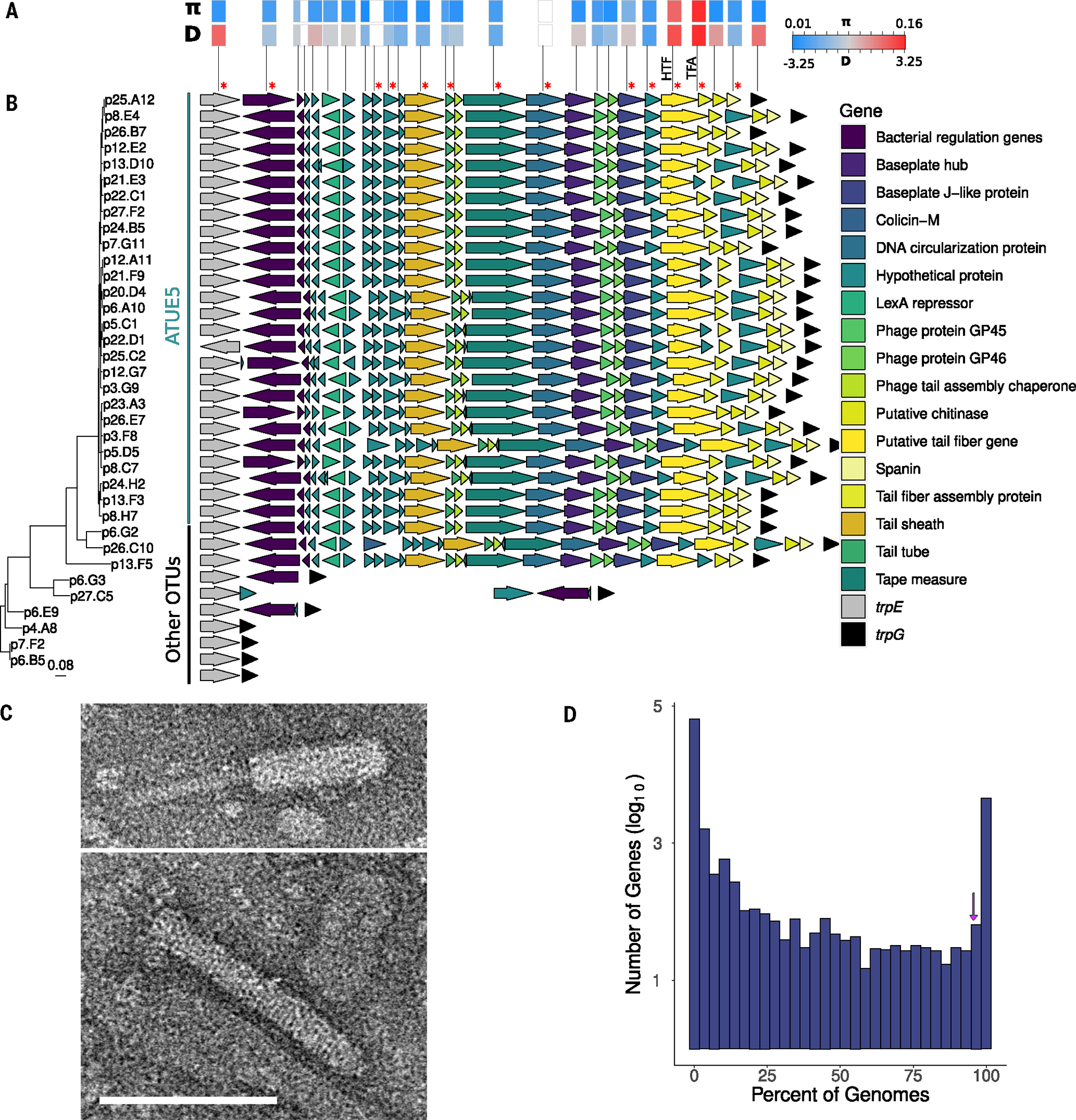
(A) Within-lineage measures of nucleotide diversity measured as pairwise nucleotide differences (π) and the site frequency spectrum measured as Tajima’s D (D) for each tailocin gene. White boxes indicate genes (statistics are excluded). Red asterisks indicate proteins found in proteomics analysis. (B) Genes of VC2 viral elements are syntenic in genomes of ATUE5. The arrows represent tailocin genes and surrounding bacterial genes (gene names are color coded in the inset). Each row is organized according to its phylogenetic placement. The phylogeny includes 36 Pseudomonas representative strains. The vertical lines indicate strains that belong to ATUE5 (green) and other OTUs (black). (C) TEM image demonstrates the presence of an assembled tailocin, showing the induced and partially purified tailocin from one representative ATUE5 strain (p25.A12) in both its contracted (top) and (bottom) uncontracted forms. Scale bar indicates 100 nm and applies to both micrographs. (D) The tailocin is part of the ATUE5 core genome. The histogram shows the frequency of each of the pangenome genes within 1399 ATUE5 genomes. The 11 most conserved tailocins genes are present in >90% of the ATUE5 genomes (marked with a purple arrow in the histogram).
