Fig. 4. The O-antigen is important for tailocin lethality and is coevolving with the tailocin HTFP.
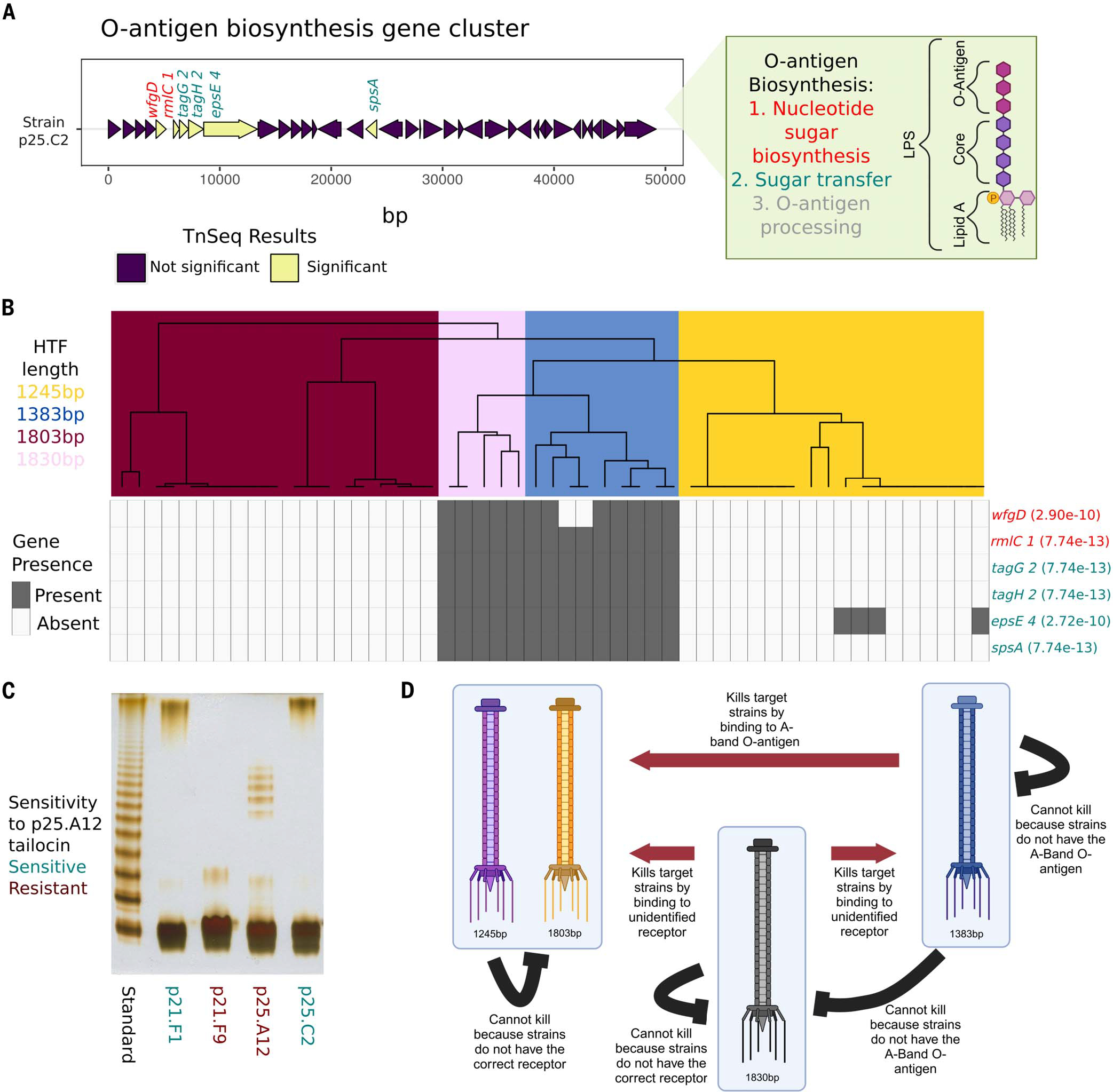
(A) Gene plot of the previously characterized O-antigen gene cluster found in the ATUE5 strains. Six of the 70 significant TnSeq genes in this study were found in this gene cluster and are shown in yellow. Gene names are colored by the step in the O-antigen biosynthesis pathway. (B) The top dendrogram is from hierarchical clustering of the PanKmer (92) output for the hypothetical tail fiber gene and colored by length. Rows represent the six significant O-antigen genes. Gray corresponds to gene presence and white to gene absence. Fisher’s exact test P values between genes and length-based clusters are shown in parentheses. (C) DOC-PAGE profile of silver-stained LPS (1 μg each lane) isolated from a subset of ATUE5 strains. The standard is of Salmonella enterica Ser. typhimurium (S-type LPS). Gray boxes indicate the high-molecular-weight O-chain. (D) Our working model of tailocin killing and lethality in P. viridiflava isolates. Red arrows indicate known significant patterns of killing. Black lines show known significant patterns of nonkilling. [Figure created with BioRender.com].
