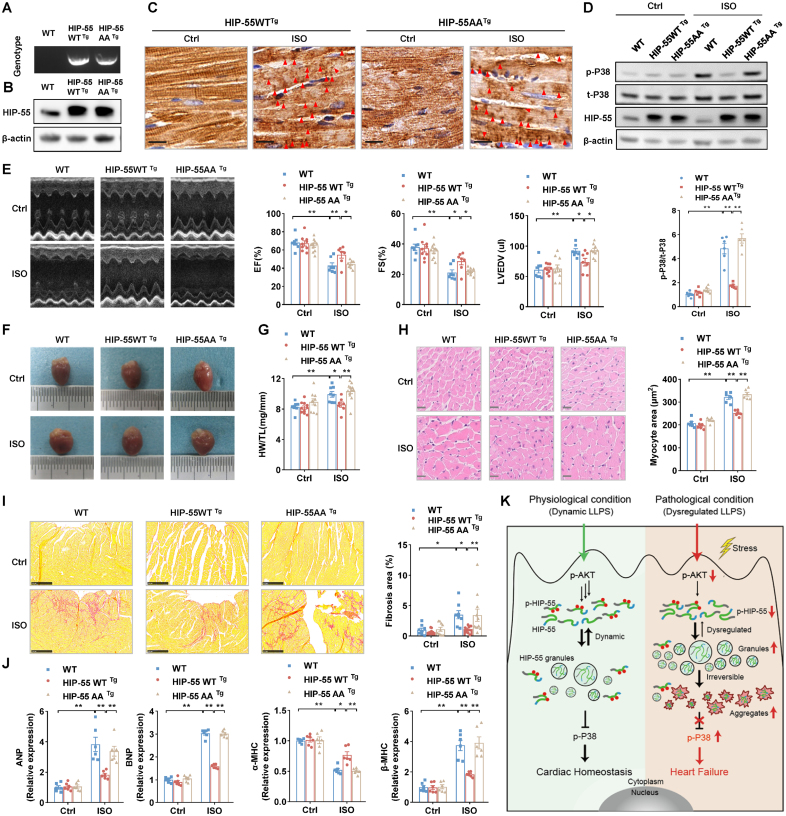
Figure 8.
Dysregulated phase separation of HIP-55 abolishes its protective function against heart failure. A, Genotypes of wild-type (WT), HIP-55WTTg, and HIP-55AATg mice. B, Detection of HIP-55 (hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1–interacting protein of 55 kDa) expression in heart tissue from WT, HIP-55WTTg, and HIP-55AATg mice. C, Immunohistochemistry staining of HIP-55 using anti–HIP-55 antibodies (dilution, 1:800) in heart tissue from control or isoproterenol (ISO)–treated transgenic mice. Arrows indicate aggregates. Scale bar=10 μm (n=6). D, Analysis of long-term ISO-induced P38 activation in heart tissue from WT, HIP-55WTTg, and HIP-55AATg mice (n=6). E, Representative M-mode echocardiographic imaging of heart and cardiac function analysis of ejection fraction (EF%), fractional shortening (FS%), and left ventricular end diastolic volume (LVEDV) after 4 weeks of ISO treatment (n=7–10). F, Gross view of WT, HIP-55WTTg, and HIP-55AATg mouse heart tissue after saline or ISO treatment for 4 weeks. G, The ratio of heart weight to tibial length (HW/TL) in WT, HIP-55WTTg, and HIP-55AATg mice (n=7–12). H, Hematoxylin & eosin staining micrographs of cross-sections of myocardia. Scale bar=20 μm (n=6). I, Representative photograph of Sirius red staining and quantification of fibrotic areas. Scale bar=250 μm (n=8–11). J, Detection of mRNA levels of heart failure marker genes (ANP, BNP, α-MHC, and β-MHC) in heart tissue from WT, HIP-55WTTg, and HIP-55AATg mice after ISO treatment (n=6). K, Working model showing phosphorylation-regulated dynamic phase separation of HIP-55 is necessary for protection against heart failure. HIP-55 possesses a strong capacity for phase separation that is dynamically regulated by AKT-mediated phosphorylation on S269/T291 in the low-complexity domain. Under physiological conditions, HIP-55 phase separation is in a dynamic equilibrium to maintain homeostasis of β-AR–mediated P38/MAPK signaling pathway activation in the heart. Under pathological conditions, prolonged excessive sympathetic hyperactivation decreases HIP-55 phosphorylation. In accordance, HIP-55 tends to form massive granules and insoluble aggregates, impairing its protective activity against heart failure. Statistical analyses were performed by 2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc correction (D, E, G, H, I, and J). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.