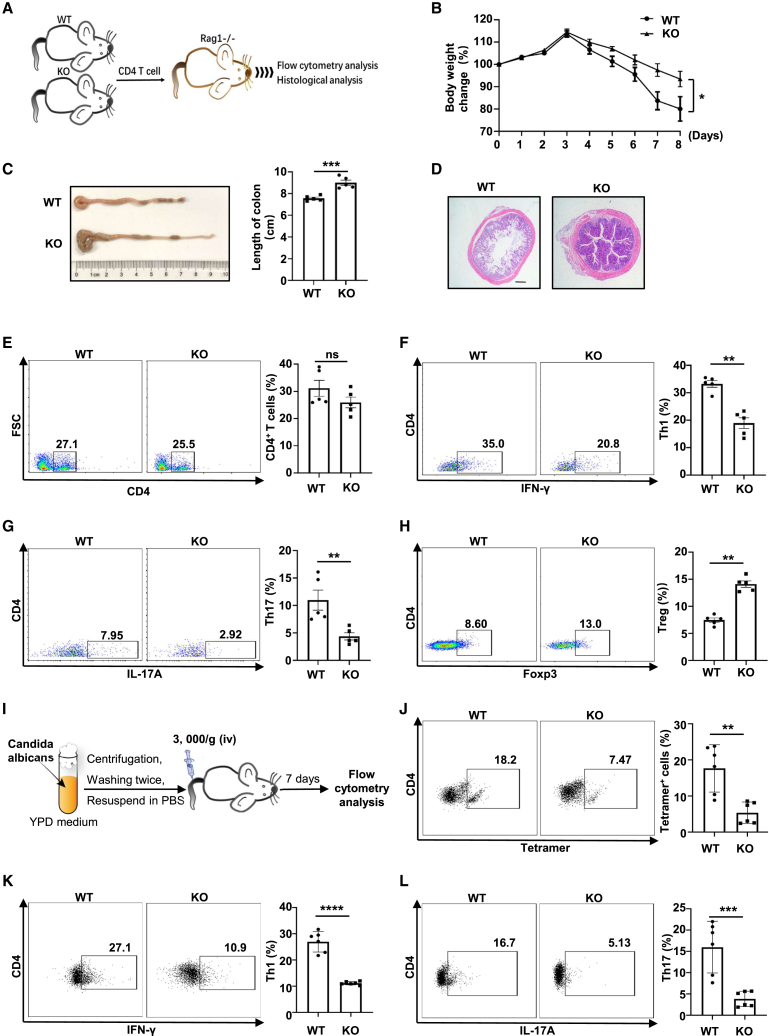
Figure 4.
Pdia3-deficient CD4 T cells are comprised in Th1 and Th17 program in vivo
(A) The scheme for the adoptive transfer experiments. (B) The percentage of body weight change of WT and KO CD4 T cell recipients. (C) Representative colon images at day 9 after adoptive transfer and quantitative analysis of colon length. (D) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of representative distal colon sections. (E–H) Mesenteric lymph nodes from WT and KO colitic mice were harvested and subjected to flow cytometry analysis. Frequencies of CD4+ T(E), CD4+IFN-γ+ (Th1) (F), CD4+IL-17A+ (Th17) (G), and CD4+Foxp3+ (Treg) (H) subsets are shown as representative dot plot graphs. (I) The scheme for C. albicans infection mouse model. (J–L) Splenocytes from infected WT and KO mice were analyzed by flow cytometry. Frequencies of CD4+ I-Ab OVA323-339 Tetramer+ CD4 T cells (J), CD4+ IFN-γ+ Th1 (K), and CD4+ IL-17A+ Th17 (L) subsets were shown as representative dot plot graphs. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated by unpaired Student’s t test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. ns, not significant.