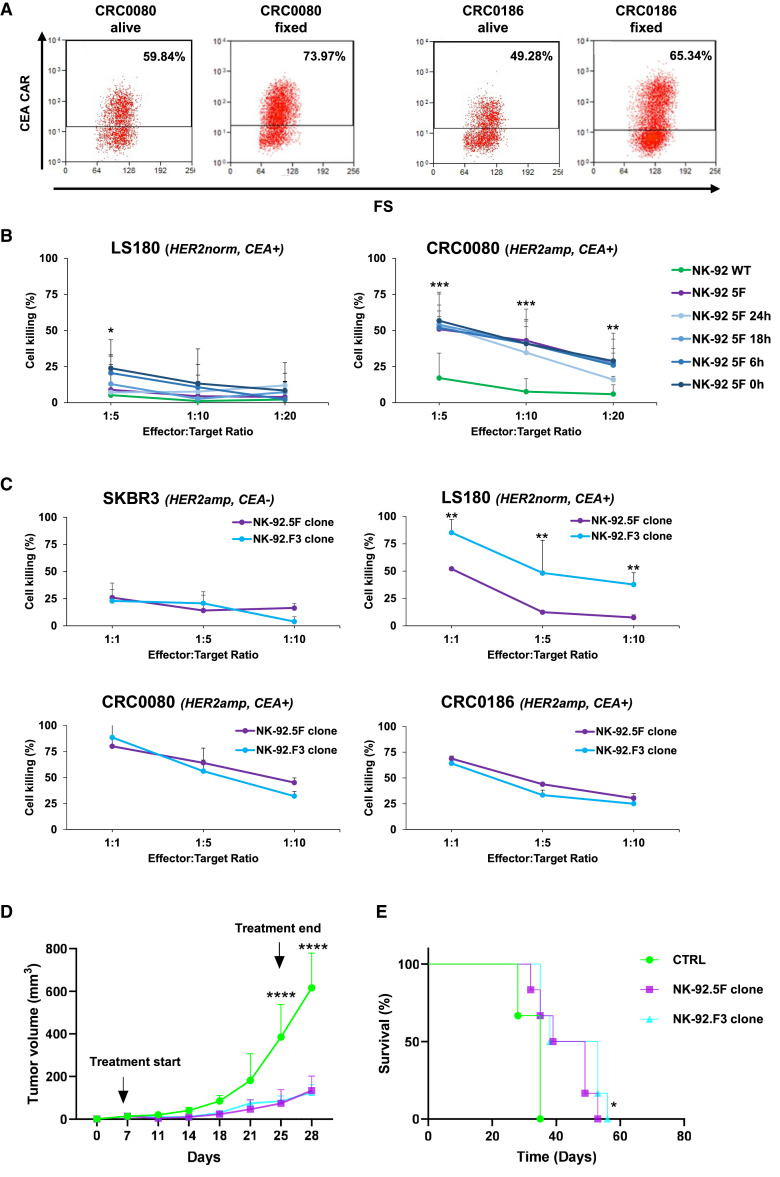
Figure 8.
Additional NK-92.5F safety and efficacy studies
(A) Flow cytometry plots displaying CEA-CAR induction in NK-92.5F after co-culture with HER2amp cells, either alive or fixed, as indicated. Numbers in the squares indicate the fraction of CEA-CAR positive-cells (two independent experiments). (B) Killing activity of irradiated NK-92.5F preactivated by incubation for 24 h on top of a monolayer of fixed HER2amp CRC0080, against CRC0080, or LS180 cells, at different time intervals after pre-activation and at different effector:target ratio, as indicated. Bars are SD (three independent experiments). (C) Killing activity of irradiated NK-92.5F and NK-92.F3 clones, against SKBR3, LS180, CRC0080, and CRC0186 cells after 48 h of co-culture at different effector:target ratios. Bars are SD (two independent experiments). (D) In vivo growth of CRC0186 xenografts treated with NK-92.5F (HER2 synNotch/CEA-CAR) or with NK-92.F3 (constitutive CEA-CAR), as indicated. We intravenously injected 5 × 106 irradiated effectors twice a week for a total of six injections, CTRL, PBS. Bars are SEM. Growth curves are stopped when the first mouse of the control cohort has reached the humane endpoint. Two-way ANOVA p values (B, C, and D): ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001, between NK-92.5F or NK-92.F3 vs. CTRL. (E) Survival curves of CRC0186 xenografts intravenously injected with 5 × 106 NK-92 irradiated effector cells, as indicated. Statistical significance between CTRL and 5F/F3 clones was calculated by log rank test for trend. ∗p ≤ 0.05.