Figure 3.
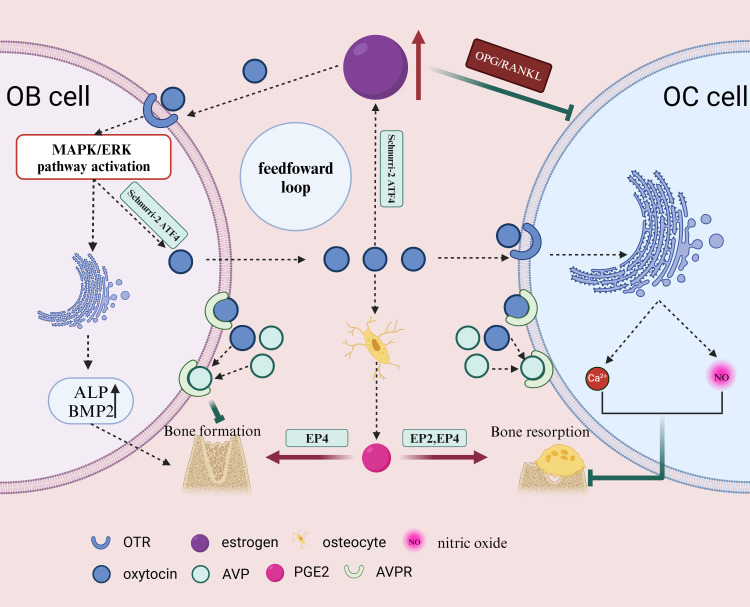
Estrogen inhibits OC bone resorption through the OPG/RANKL pathway and can stimulate bone formation at higher doses. OB, when influenced by estrogen, typically reactively produces OT, which further amplifies the effects of estrogen, increases OT production, and forms an estrogen-mediated OT positive feedback loop. AVPR-1a and -2a are expressed in OBs and bone cells. OT and AVP compete for the same receptors on OB, exerting opposite effects. OT can also stimulate bone cells to secrete prostaglandins, promote OB differentiation, and enhance osteogenic ability. OT can induce PGE2 synthesis in bone cells, and PGE2 regulates bone formation and resorption through EP2 and EP4 receptors. After stimulating mature OC, OT can inhibit OC by triggering intracellular Ca2+ release and nitric oxide synthesis. This illustration created with BioRender (https://biorender.com).