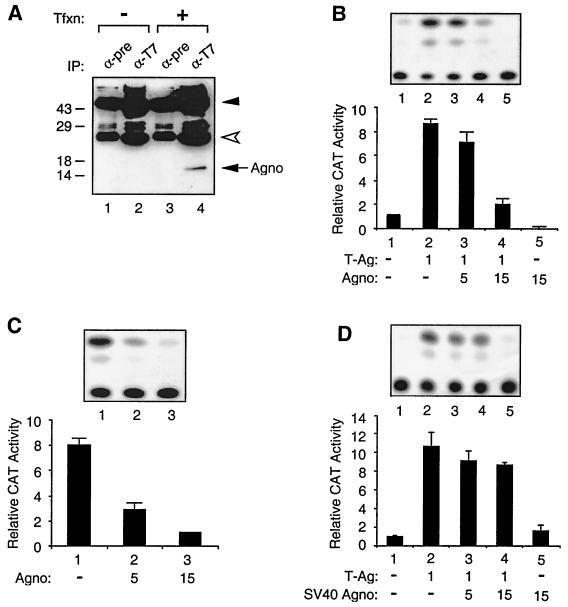
FIG. 2.
Effect of Agno protein on transcriptional activity of the JCV late promoter. (A) Expression of JCV Agno gene. pEBV-His-Agno expression plasmid was introduced into U-87MG cells. Two hundred micrograms of whole-cell extracts prepared from untransfected (lanes 1 and 2) and transfected (lanes 3 and 4) cells was immunoprecipitated with either preimmune (α-pre) (lanes 1 and 3) or anti-T7 (α-T7) (lanes 2 and 4) antibodies. Immunocomplexes were resolved by an SDS–15% PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-T7 antibody. Tfxn, transfection; IP, immunoprecipitation. Closed and open arrowheads indicate large and small IgG fragments, respectively. The arrow indicates His-tagged Agno. The positions of molecular mass markers (in Kilodaltons) are shown to the left of the panel. (B) Agno suppresses T-antigen-mediated transactivation of JCV late promoter. A reporter plasmid (pBLCAT3-Mad-1L) (7 μg) was introduced into U-87MG cells alone or in combination with plasmids expressing Agno protein and T antigen (T-Ag) as indicated for each lane. At 36 h posttransfection, CAT enzymatic activity was determined. (C) Agno protein suppresses the basal expression of JCV late promoter. pBLCAT3-Mad-1L reporter plasmid (10 μg) was introduced into U-87MG cells alone or together with 5 and 15 μg of Agno protein expression plasmid. Bar graph shows CAT values relative to the basal expression of the reporter construct alone. (D) Effect of SV40 Agno protein on T-antigen-mediated activation of JCV late promoter. Transfections were carried out as described for Fig. 2B. The results of a representative CAT assay for each panel (B, C, and D) are shown on top. Results shown in each panel represent the mean of three independent experiments and bars indicate standard deviation.