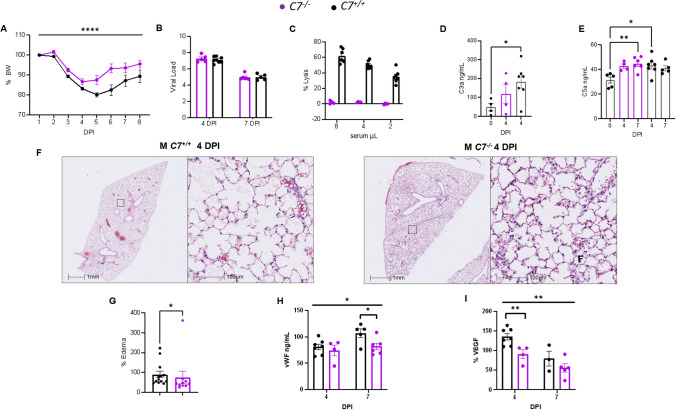
Fig. 5.
Deficiency of C7 protects against severe COVID-19. A–I Mixed sex C7+/+ (n = 14, 10 males, 4 females) and C7−/− mice (n=11, 7 males, 4 females) aged 15–17 weeks were infected with an infectious dose of MA30 SARS-CoV-2 (2.5×104 TCID50) and euthanized at 4 and 7 DPI. A Percent body weight changes as assessed by Two-way ANOVA. B viral load after infection as measured by qPCR. C Hemolytic assay showing complement activity as measured by serial dilution of the infected sera as a source of the complement to lyse the anti-body sensitized sheep erythrocytes. D-E C3a (D) and C5a (E) measurements of the sera from the infected mice by ELISA with significant differences as assessed by One-way ANOVA with Dunnet’s (D) or Tukey’s (E) multiple comparisons. F-G Representative images of pulmonary edema at 4 DPI (F) and quantification (G) analyzed by Student t-test. H-I vWF (H) and VEGF (I) serum levels (ng/mL) at 4 and 7 DPI. Overall signficiance assessed by One-way ANOVA and indicated by horizontal bar with individual comparisons assessed by two-tailed Student t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001