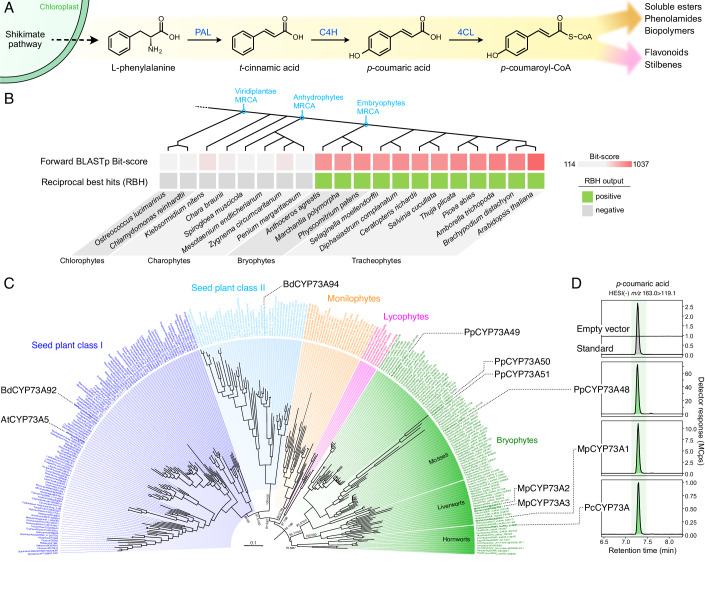
Figure 1. Evolutionary history of the CYP73 family encoding t-cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase.
(A) Schematic representation of the three steps of the general phenylpropanoid pathway. PAL, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase; C4H, cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase; 4CL, 4-coumarate:CoA ligase. (B) Search for AtCYP73A5 homologs in Viridiplantae by a reciprocal best hit (RBH) strategy. MRCA, most recent common ancestor. (C) Maximum-likelihood nucleotide tree (IQ-TREE2, GTR + F + I + R7) describing the phylogenetic relationships between 275 CYP73 homologous sequences. SH-aLRT test and ultrafast bootstrap (1000 pseudo-replicates) supports are annotated on main branches. CYP73 homologs relevant to the present study are indicated. At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Bd, Brachypodium distachyon; Mp, Marchantia polymorpha; Pc, Phaeoceros carolinianus. Scale bar represents the number of nucleotide substitutions per site. Tree was rooted according to the midpoint method. (D) Representative UHPLC-MS/MS chromatograms showing the production in vitro of p-coumaric acid from t-cinnamic acid (C4H activity) by recombinant CYP73 proteins representative of the three major bryophyte groups: mosses (PpCYP73A48), liverworts (MpCYP73A1) and hornworts (PcCYP73A). Assays performed with microsomes derived from yeasts transformed with an empty vector were used as negative controls. Source data are available online for this figure.