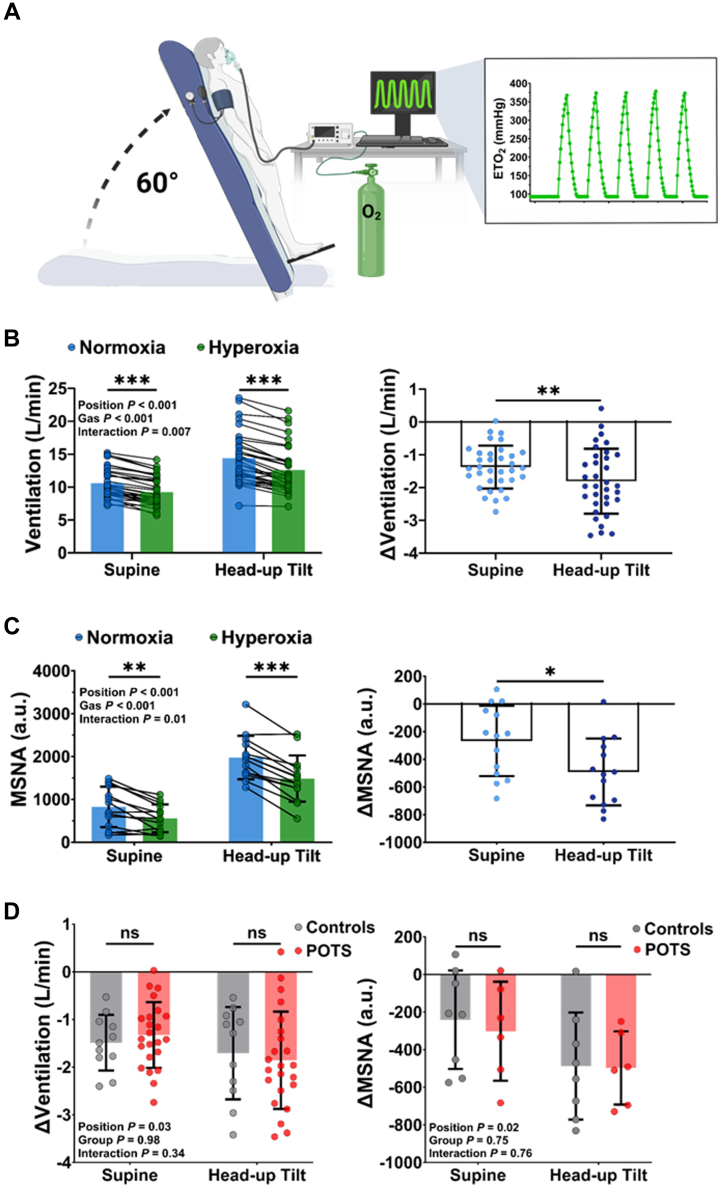
Figure 2.
Sympathorespiratory Responses to Peripheral Chemoreceptor Inhibition
(A) Hyperoxia was supplied using sequential gas delivery to precisely control acute, transient bouts of oxygen while participants were supine and upright. (B) Across the cohort, hyperoxia significantly reduced ventilation in the supine and upright positions (left), and the ventilatory reduction was greater during head-up tilt (right). (C) Pooled MSNA responses to hyperoxia were also reduced in the supine and upright position (left) and were similar reduced to a greater magnitude during head-up tilt (right). (D) Between-group comparisons showed that neither the magnitude of ventilation inhibition (left) nor sympathetic inhibition (right) was different between patients with POTS and control subjects in either position. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Pooled ventilatory and MSNA responses to hyperoxia and group differences in ventilation and MSNA inhibition during hyperoxia were compared using a 2-factor mixed-effects model with Bonferroni post hoc testing correction. Abbreviations as in Figure 1.