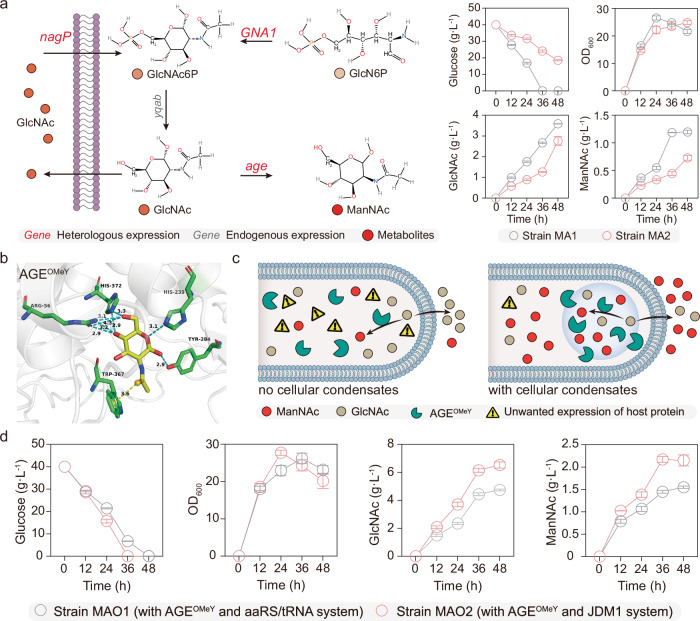
Fig. 6. Improving translation specificity of AGEOMeY involving N-acetylmannosamine biosynthesis.
a Shake flask fermentation of ManNAc by strains MA1 and MA2. The gene GNA1 and age were integrated into the genome of the engineered strain S5, generating strain MA1. Besides, the original aaRS/tRNAOMeY system was expressed in MA1, yielding the strain MA2. GlcN6P glucosamine-6-phosphate, GlcNAc N-acetylglucosamine, GlcNAc6P GlcNAc-6-phosphate, ManNAc N-acetylmannosamine, GNA1 GlcN6P N-acetyltransferase, AGE N-acylglucosamine 2-epimerase, yqab, hydrolase-like phosphatase, nagP phosphotransferase system GlcNAc-specific transporter subunit EIICB, OMeY O-methyl-L-tyrosine. b The Rosetta-predicted combined mutant AGEOMeY with GlcNAc bound is shown. The blue dotted line means hydrogen-bonding, and the yellow dotted line means pi interactions. c Illustration of synthetic functional condensates to increase translation specificity of enzyme AGEOMeY for improving the ManNAc biosynthesis. d Trends of cell growth, glucose, GlcNAc, and ManNAc concentration of the strains MAO1 and MAO2. Data are presented as mean ± s.d. of three biologically independent replicates. Source data provided as a Source Data file.